TreyNet: A Neural Model for Text Localization, Transcription and Named Entity Recognition in Full Pages
Paper and Code
Dec 20, 2019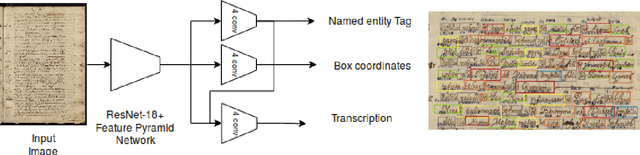
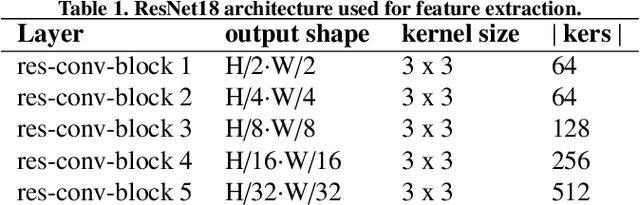
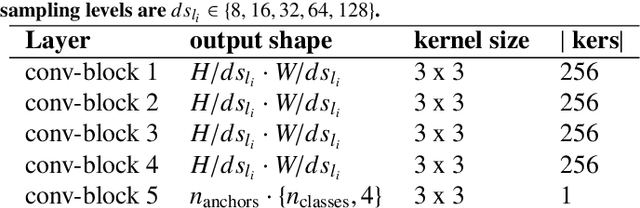
In the last years, the consolidation of deep neural network architectures for information extraction in document images has brought big improvements in the performance of each of the tasks involved in this process, consisting of text localization, transcription, and named entity recognition. However, this process is traditionally performed with separate methods for each task. In this work we propose an end-to-end model that jointly performs handwritten text detection, transcription, and named entity recognition at page level, capable of benefiting from shared features for these tasks. We exhaustively evaluate our approach on different datasets, discussing its advantages and limitations compared to sequential approaches.
* Submitted to Pattern Recognition Letters
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge