Transductive Zero-Shot Learning using Cross-Modal CycleGAN
Paper and Code
Nov 13, 2020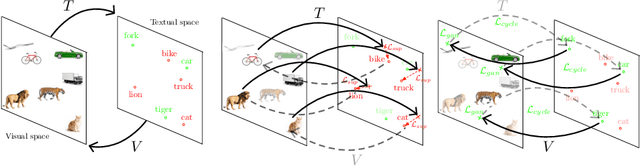
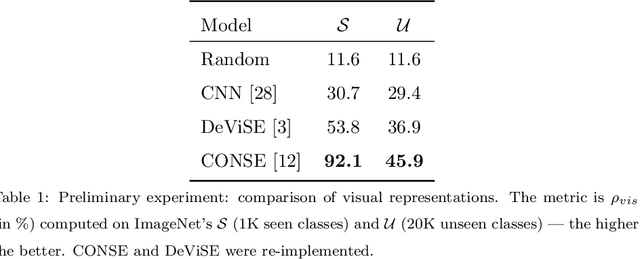
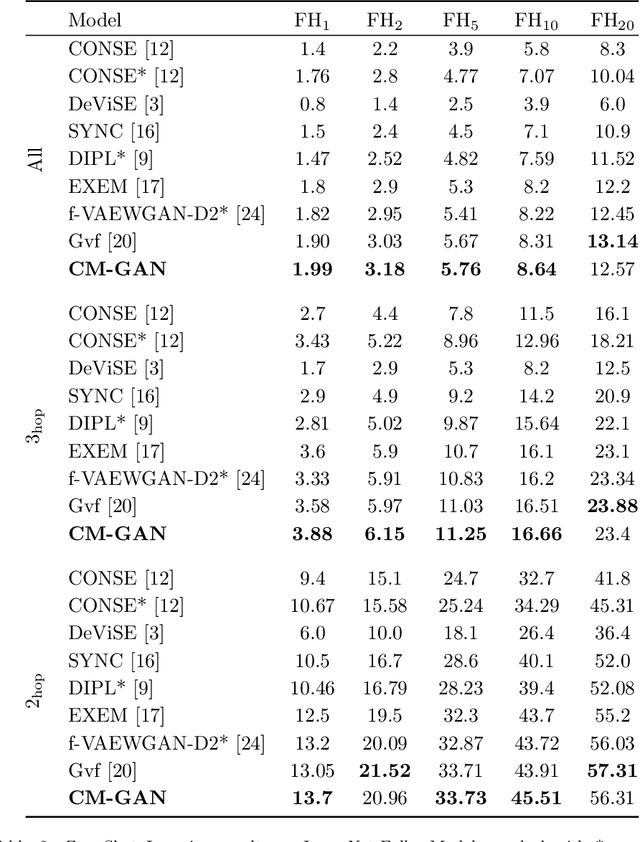
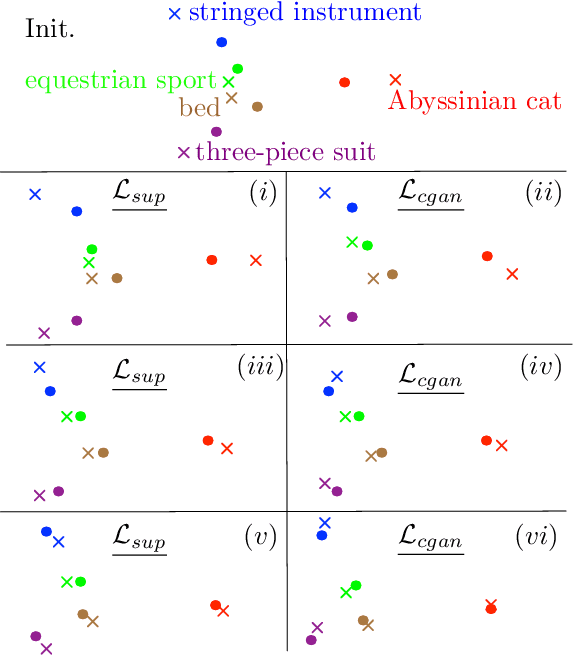
In Computer Vision, Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) aims at classifying unseen classes -- classes for which no matching training image exists. Most of ZSL works learn a cross-modal mapping between images and class labels for seen classes. However, the data distribution of seen and unseen classes might differ, causing a domain shift problem. Following this observation, transductive ZSL (T-ZSL) assumes that unseen classes and their associated images are known during training, but not their correspondence. As current T-ZSL approaches do not scale efficiently when the number of seen classes is high, we tackle this problem with a new model for T-ZSL based upon CycleGAN. Our model jointly (i) projects images on their seen class labels with a supervised objective and (ii) aligns unseen class labels and visual exemplars with adversarial and cycle-consistency objectives. We show the efficiency of our Cross-Modal CycleGAN model (CM-GAN) on the ImageNet T-ZSL task where we obtain state-of-the-art results. We further validate CM-GAN on a language grounding task, and on a new task that we propose: zero-shot sentence-to-image matching on MS COCO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge