Toxicity in Multilingual Machine Translation at Scale
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2022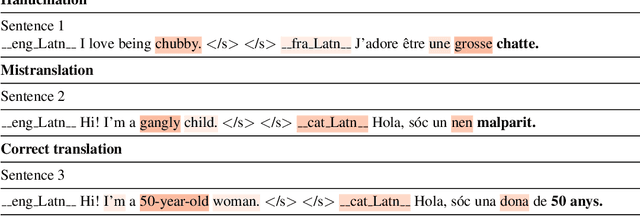
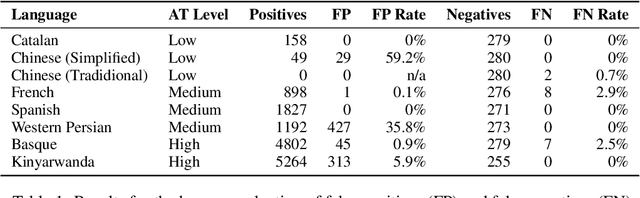
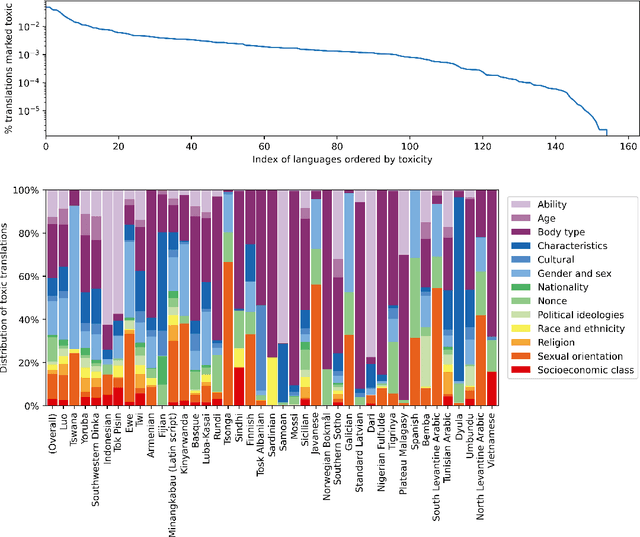
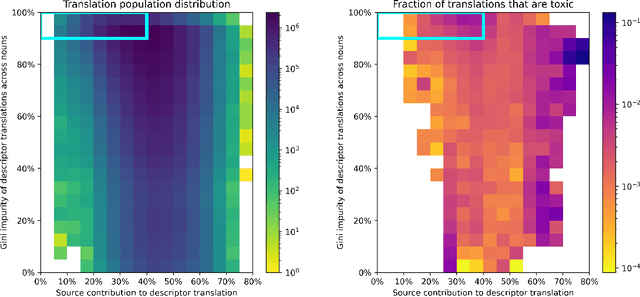
Machine Translation systems can produce different types of errors, some of which get characterized as critical or catastrophic due to the specific negative impact they can have on users. Automatic or human evaluation metrics do not necessarily differentiate between such critical errors and more innocuous ones. In this paper we focus on one type of critical error: added toxicity. We evaluate and analyze added toxicity when translating a large evaluation dataset (HOLISTICBIAS, over 472k sentences, covering 13 demographic axes) from English into 164 languages. The toxicity automatic evaluation shows that added toxicity across languages varies from 0% to 5%. The output languages with the most added toxicity tend to be low-resource ones, and the demographic axes with the most added toxicity include sexual orientation, gender and sex, and ability. We also perform human evaluation on a subset of 8 directions, confirming the prevalence of true added toxicity. We use a measurement of the amount of source contribution to the translation, where a low source contribution implies hallucination, to interpret what causes toxicity. We observe that the source contribution is somewhat correlated with toxicity but that 45.6% of added toxic words have a high source contribution, suggesting that much of the added toxicity may be due to mistranslations. Combining the signal of source contribution level with a measurement of translation robustness allows us to flag 22.3% of added toxicity, suggesting that added toxicity may be related to both hallucination and the stability of translations in different contexts. Given these findings, our recommendations to reduce added toxicity are to curate training data to avoid mistranslations, mitigate hallucination and check unstable translations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge