Towards Robust Autonomous Grasping with Reflexes Using High-Bandwidth Sensing and Actuation
Paper and Code
Sep 23, 2022
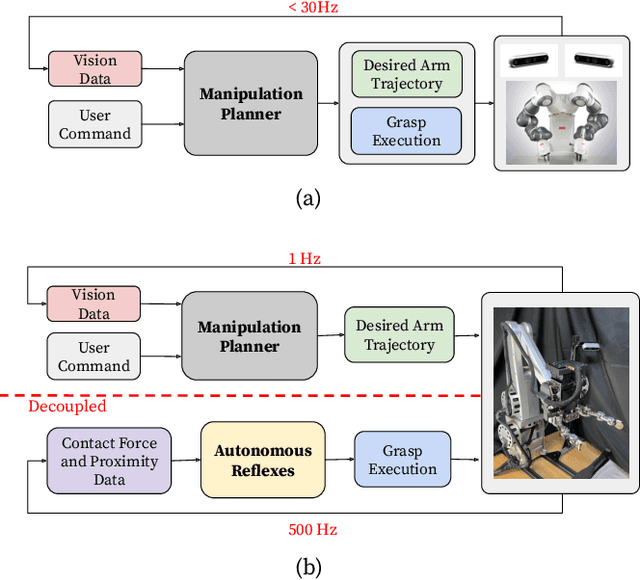
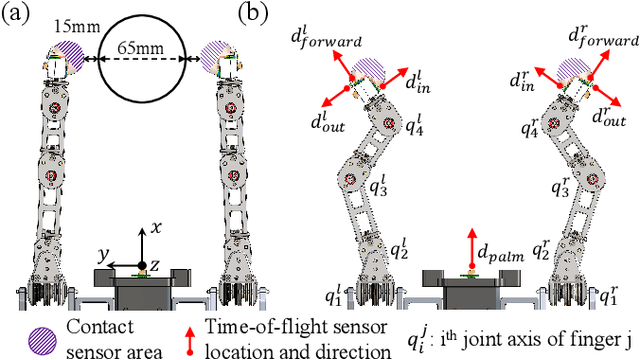
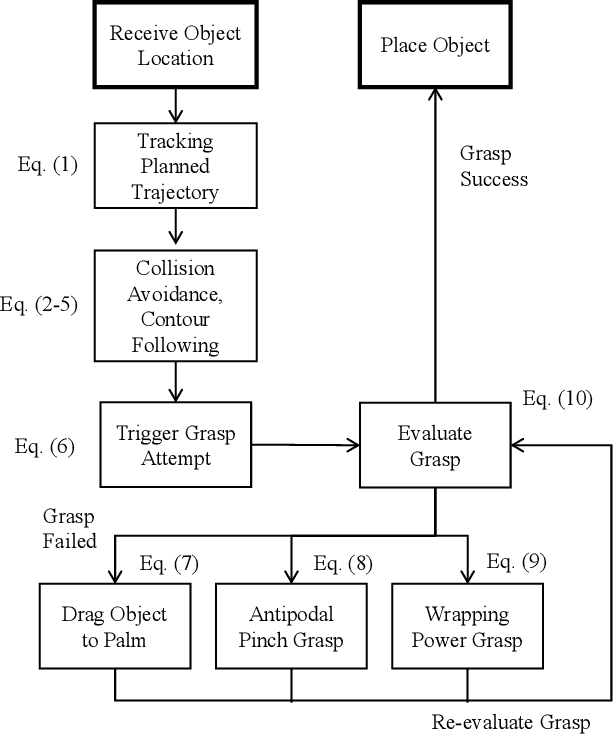
Modern robotic manipulation systems fall short of human manipulation skills partly because they rely on closing feedback loops exclusively around vision data, which reduces system bandwidth and speed. By developing autonomous grasping reflexes that rely on high-bandwidth force, contact, and proximity data, the overall system speed and robustness can be increased while reducing reliance on vision data. We are developing a new system built around a low-inertia, high-speed arm with nimble fingers that combines a high-level trajectory planner operating at less than 1 Hz with low-level autonomous reflex controllers running upwards of 300 Hz. We characterize the reflex system by comparing the volume of the set of successful grasps for a naive baseline controller and variations of our reflexive grasping controller, finding that our controller expands the set of successful grasps by 55% relative to the baseline. We also deploy our reflexive grasping controller with a simple vision-based planner in an autonomous clutter clearing task, achieving a grasp success rate above 90% while clearing over 100 items.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge