Towards Psychologically-Grounded Dynamic Preference Models
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2022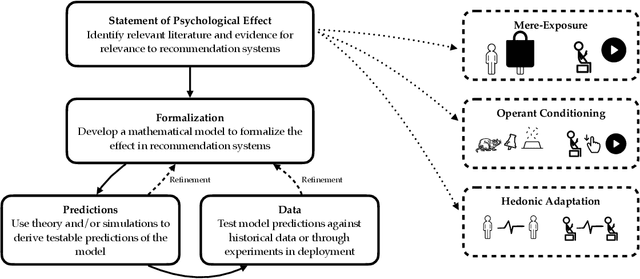
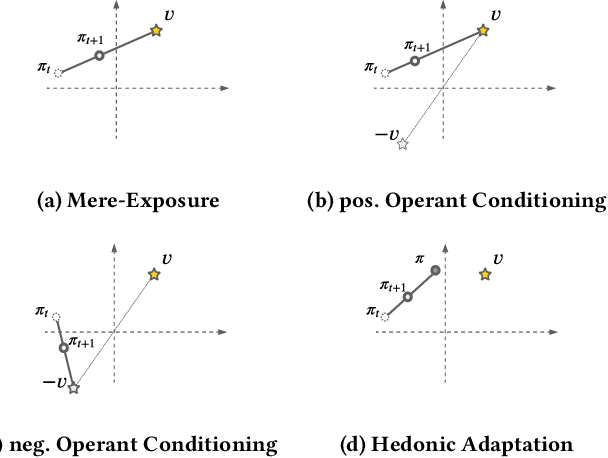
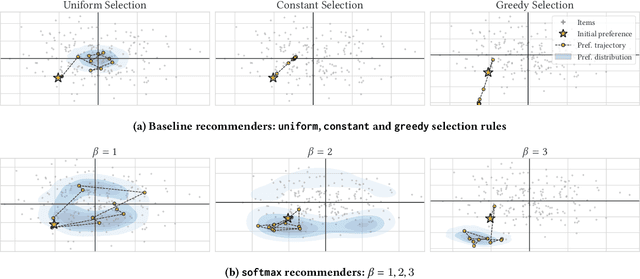
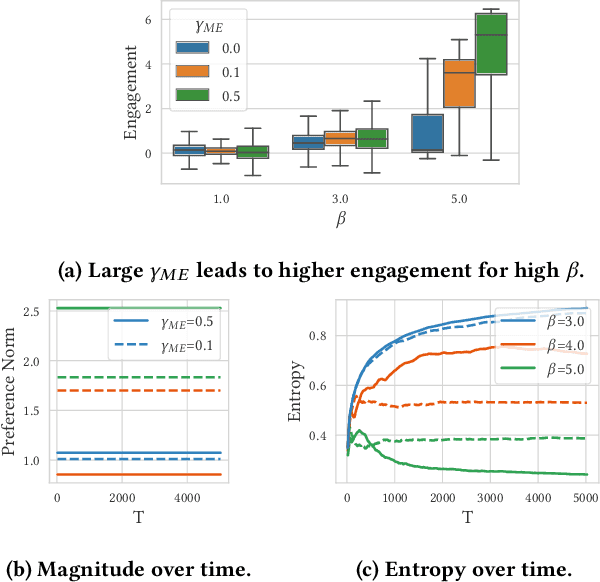
Designing recommendation systems that serve content aligned with time varying preferences requires proper accounting of the feedback effects of recommendations on human behavior and psychological condition. We argue that modeling the influence of recommendations on people's preferences must be grounded in psychologically plausible models. We contribute a methodology for developing grounded dynamic preference models. We demonstrate this method with models that capture three classic effects from the psychology literature: Mere-Exposure, Operant Conditioning, and Hedonic Adaptation. We conduct simulation-based studies to show that the psychological models manifest distinct behaviors that can inform system design. Our study has two direct implications for dynamic user modeling in recommendation systems. First, the methodology we outline is broadly applicable for psychologically grounding dynamic preference models. It allows us to critique recent contributions based on their limited discussion of psychological foundation and their implausible predictions. Second, we discuss implications of dynamic preference models for recommendation systems evaluation and design. In an example, we show that engagement and diversity metrics may be unable to capture desirable recommendation system performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge