Towards learning domain-independent planning heuristics
Paper and Code
Jul 21, 2017
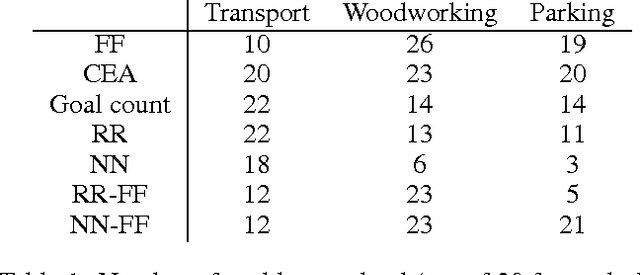
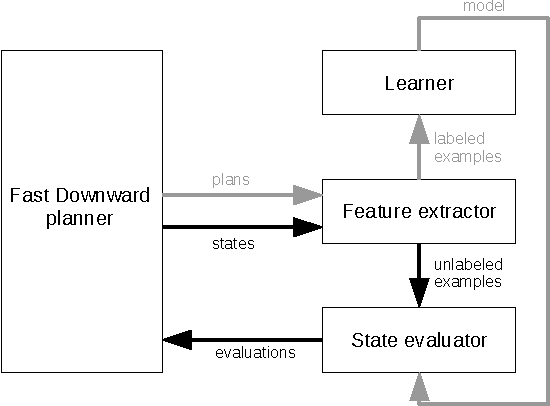
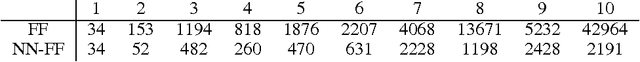
Automated planning remains one of the most general paradigms in Artificial Intelligence, providing means of solving problems coming from a wide variety of domains. One of the key factors restricting the applicability of planning is its computational complexity resulting from exponentially large search spaces. Heuristic approaches are necessary to solve all but the simplest problems. In this work, we explore the possibility of obtaining domain-independent heuristic functions using machine learning. This is a part of a wider research program whose objective is to improve practical applicability of planning in systems for which the planning domains evolve at run time. The challenge is therefore the learning of (corrections of) domain-independent heuristics that can be reused across different planning domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge