Towards Biologically Plausible Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2016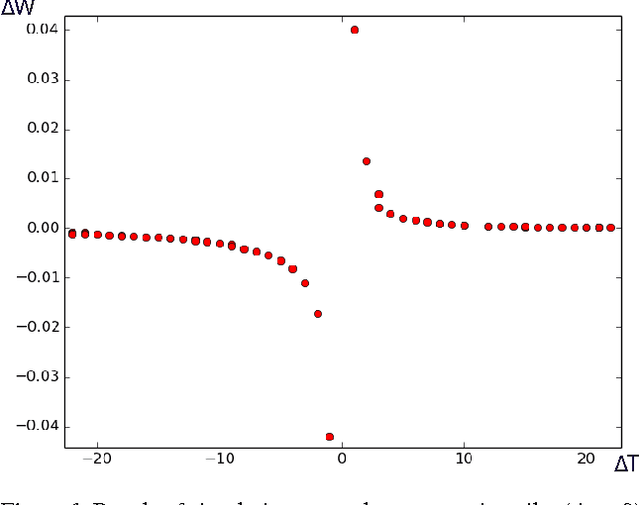
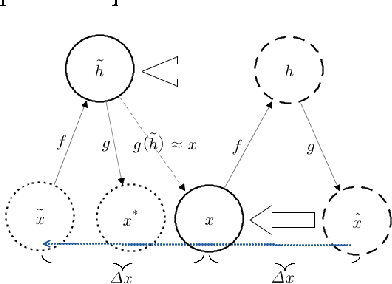

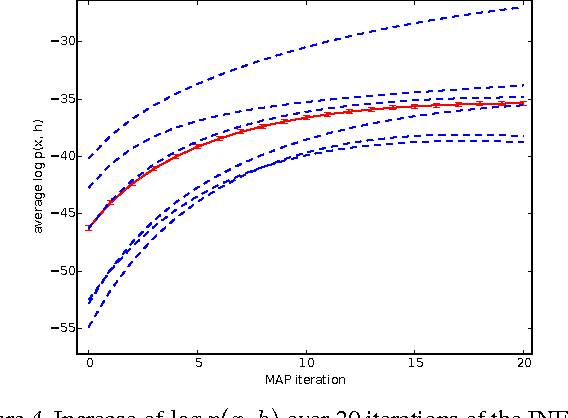
Neuroscientists have long criticised deep learning algorithms as incompatible with current knowledge of neurobiology. We explore more biologically plausible versions of deep representation learning, focusing here mostly on unsupervised learning but developing a learning mechanism that could account for supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning. The starting point is that the basic learning rule believed to govern synaptic weight updates (Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity) arises out of a simple update rule that makes a lot of sense from a machine learning point of view and can be interpreted as gradient descent on some objective function so long as the neuronal dynamics push firing rates towards better values of the objective function (be it supervised, unsupervised, or reward-driven). The second main idea is that this corresponds to a form of the variational EM algorithm, i.e., with approximate rather than exact posteriors, implemented by neural dynamics. Another contribution of this paper is that the gradients required for updating the hidden states in the above variational interpretation can be estimated using an approximation that only requires propagating activations forward and backward, with pairs of layers learning to form a denoising auto-encoder. Finally, we extend the theory about the probabilistic interpretation of auto-encoders to justify improved sampling schemes based on the generative interpretation of denoising auto-encoders, and we validate all these ideas on generative learning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge