Towards Automatic Prediction of Outcome in Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms
Paper and Code
Nov 18, 2022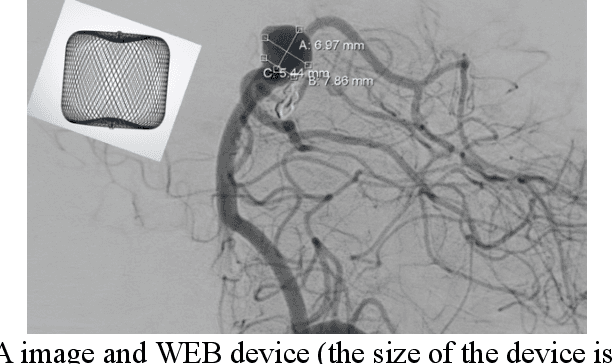
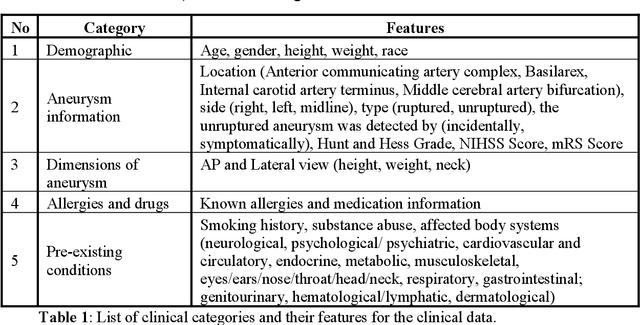
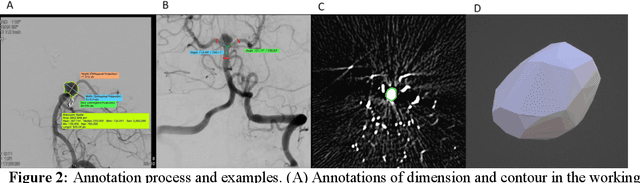
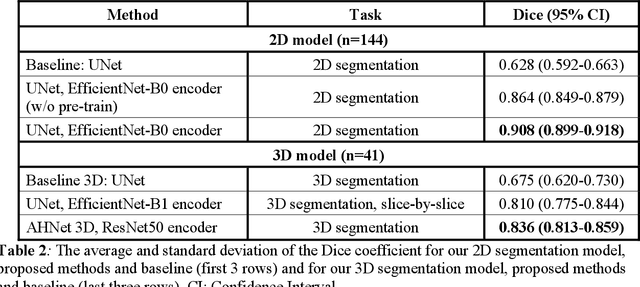
Intrasaccular flow disruptors treat cerebral aneurysms by diverting the blood flow from the aneurysm sac. Residual flow into the sac after the intervention is a failure that could be due to the use of an undersized device, or to vascular anatomy and clinical condition of the patient. We report a machine learning model based on over 100 clinical and imaging features that predict the outcome of wide-neck bifurcation aneurysm treatment with an intravascular embolization device. We combine clinical features with a diverse set of common and novel imaging measurements within a random forest model. We also develop neural network segmentation algorithms in 2D and 3D to contour the sac in angiographic images and automatically calculate the imaging features. These deliver 90% overlap with manual contouring in 2D and 83% in 3D. Our predictive model classifies complete vs. partial occlusion outcomes with an accuracy of 75.31%, and weighted F1-score of 0.74.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge