Through-Wall Imaging based on WiFi Channel State Information
Paper and Code
Jan 30, 2024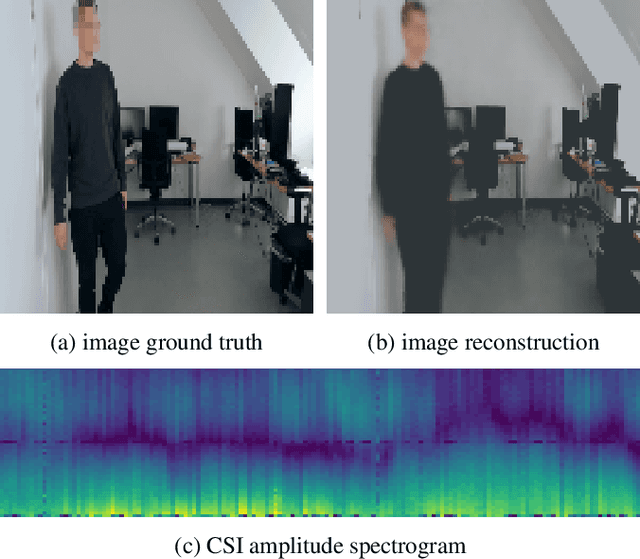
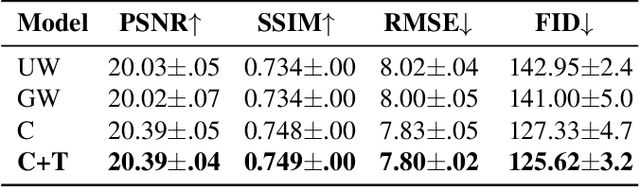
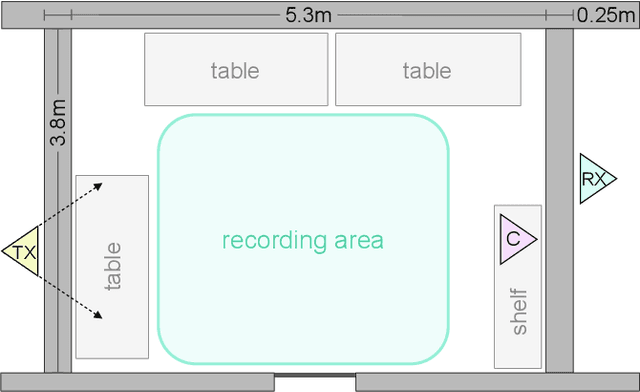
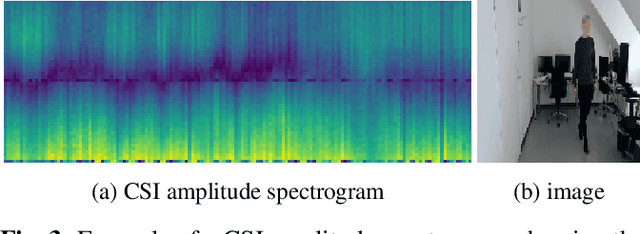
This work presents a seminal approach for synthesizing images from WiFi Channel State Information (CSI) in through-wall scenarios. Leveraging the strengths of WiFi, such as cost-effectiveness, illumination invariance, and wall-penetrating capabilities, our approach enables visual monitoring of indoor environments beyond room boundaries and without the need for cameras. More generally, it improves the interpretability of WiFi CSI by unlocking the option to perform image-based downstream tasks, e.g., visual activity recognition. In order to achieve this crossmodal translation from WiFi CSI to images, we rely on a multimodal Variational Autoencoder (VAE) adapted to our problem specifics. We extensively evaluate our proposed methodology through an ablation study on architecture configuration and a quantitative/qualitative assessment of reconstructed images. Our results demonstrate the viability of our method and highlight its potential for practical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge