Think Locally, Act Globally: Federated Learning with Local and Global Representations
Paper and Code
Jan 06, 2020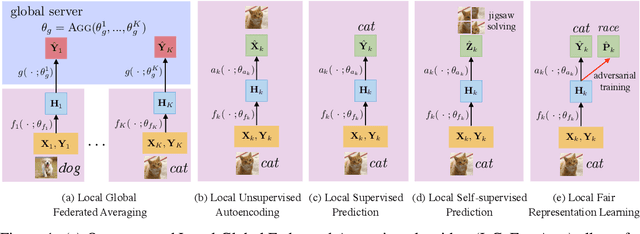
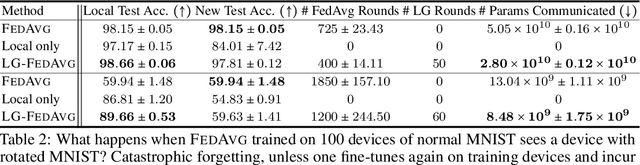
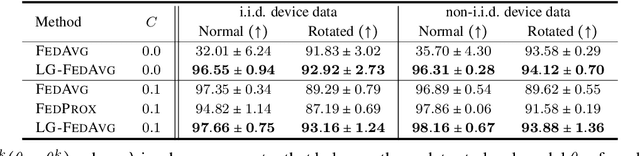
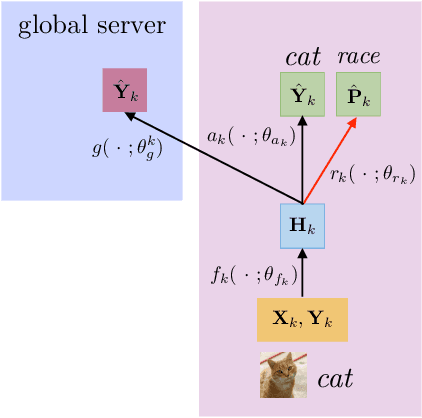
Federated learning is an emerging research paradigm to train models on private data distributed over multiple devices. A key challenge involves keeping private all the data on each device and training a global model only by communicating parameters and updates. Overcoming this problem relies on the global model being sufficiently compact so that the parameters can be efficiently sent over communication channels such as wireless internet. Given the recent trend towards building deeper and larger neural networks, deploying such models in federated settings on real-world tasks is becoming increasingly difficult. To this end, we propose to augment federated learning with local representation learning on each device to learn useful and compact features from raw data. As a result, the global model can be smaller since it only operates on higher-level local representations. We show that our proposed method achieves superior or competitive results when compared to traditional federated approaches on a suite of publicly available real-world datasets spanning image recognition (MNIST, CIFAR) and multimodal learning (VQA). Our choice of local representation learning also reduces the number of parameters and updates that need to be communicated to and from the global model, thereby reducing the bottleneck in terms of communication cost. Finally, we show that our local models provide flexibility in dealing with online heterogeneous data and can be easily modified to learn fair representations that obfuscate protected attributes such as race, age, and gender, a feature crucial to preserving the privacy of on-device data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge