The LoDoPaB-CT Dataset: A Benchmark Dataset for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction Methods
Paper and Code
Oct 01, 2019
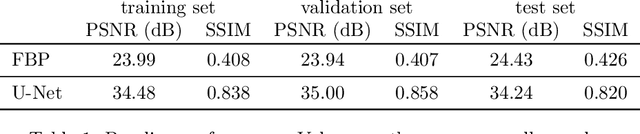
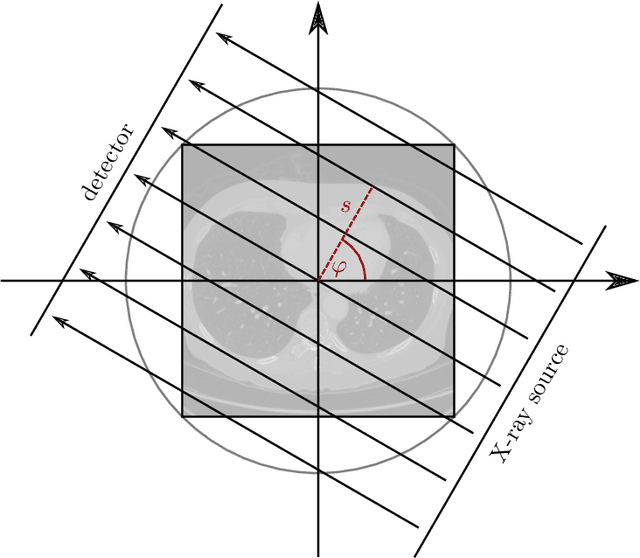
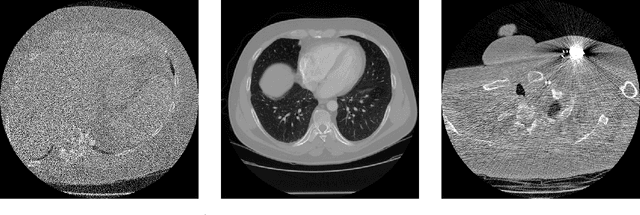
Deep Learning approaches for solving Inverse Problems in imaging have become very effective and are demonstrated to be quite competitive in the field. Comparing these approaches is a challenging task since they highly rely on the data and the setup that is used for training. We provide a public dataset of computed tomography images and simulated low-dose measurements suitable for training this kind of methods. With the LoDoPaB-CT Dataset we aim to create a benchmark that allows for a fair comparison. It contains over 40,000 scan slices from around 800 patients selected from the LIDC/IDRI Database. In this paper we describe how we processed the original slices and how we simulated the measurements. We also include first baseline results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge