The Gender Gap in Face Recognition Accuracy Is a Hairy Problem
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2022
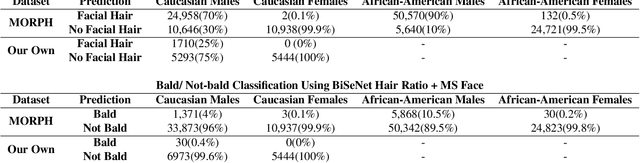
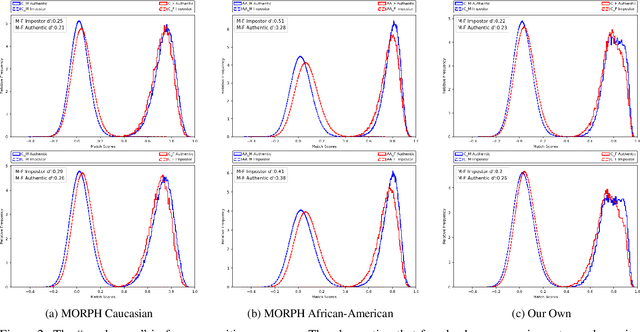
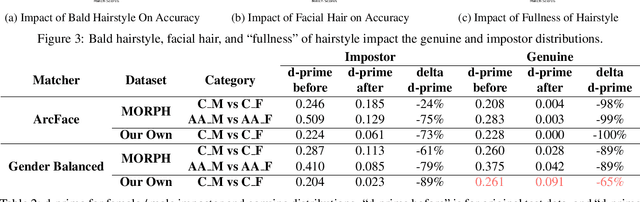
It is broadly accepted that there is a "gender gap" in face recognition accuracy, with females having higher false match and false non-match rates. However, relatively little is known about the cause(s) of this gender gap. Even the recent NIST report on demographic effects lists "analyze cause and effect" under "what we did not do". We first demonstrate that female and male hairstyles have important differences that impact face recognition accuracy. In particular, compared to females, male facial hair contributes to creating a greater average difference in appearance between different male faces. We then demonstrate that when the data used to estimate recognition accuracy is balanced across gender for how hairstyles occlude the face, the initially observed gender gap in accuracy largely disappears. We show this result for two different matchers, and analyzing images of Caucasians and of African-Americans. These results suggest that future research on demographic variation in accuracy should include a check for balanced quality of the test data as part of the problem formulation. To promote reproducible research, matchers, attribute classifiers, and datasets used in this research are/will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge