The Effect of Perceptual Metrics on Music Representation Learning for Genre Classification
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2024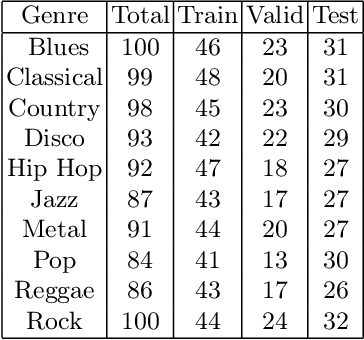
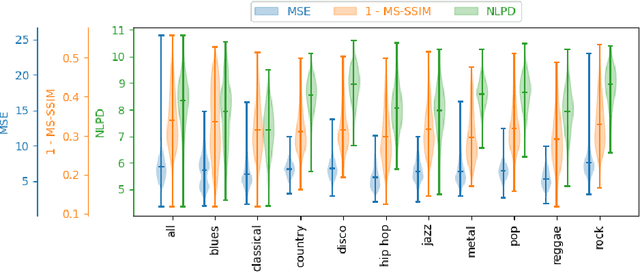
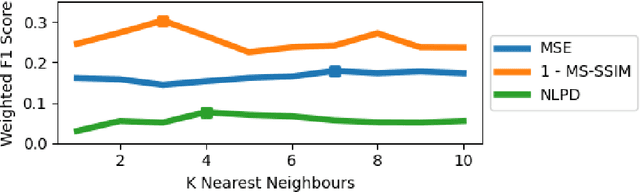
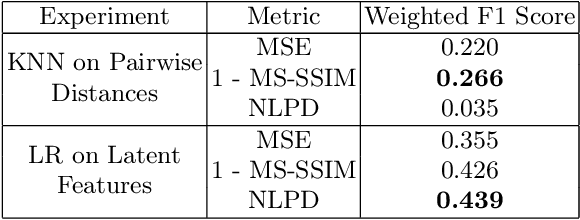
The subjective quality of natural signals can be approximated with objective perceptual metrics. Designed to approximate the perceptual behaviour of human observers, perceptual metrics often reflect structures found in natural signals and neurological pathways. Models trained with perceptual metrics as loss functions can capture perceptually meaningful features from the structures held within these metrics. We demonstrate that using features extracted from autoencoders trained with perceptual losses can improve performance on music understanding tasks, i.e. genre classification, over using these metrics directly as distances when learning a classifier. This result suggests improved generalisation to novel signals when using perceptual metrics as loss functions for representation learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge