The ApolloScape Open Dataset for Autonomous Driving and its Application
Paper and Code
Sep 26, 2018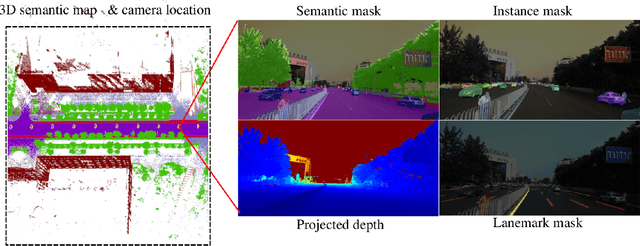
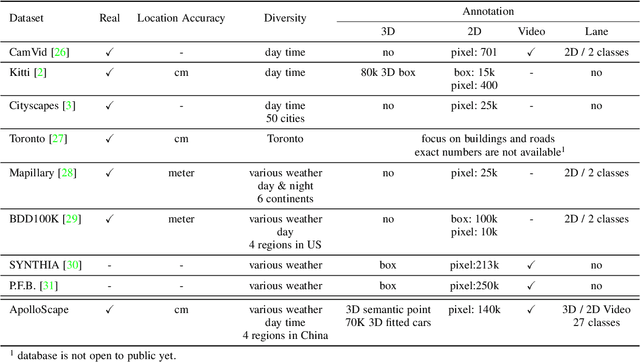
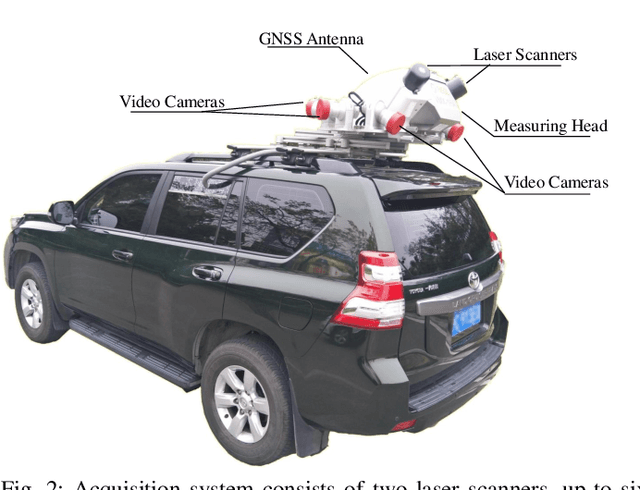
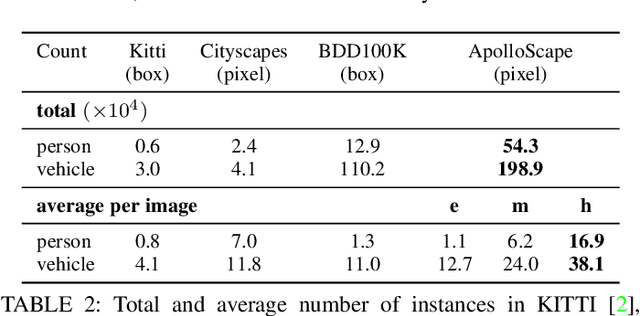
Autonomous driving has attracted tremendous attention especially in the past few years. The key techniques for a self-driving car include solving tasks like 3D map construction, self-localization, parsing the driving road and understanding objects, which enable vehicles to reason and act. However, large scale data set for training and system evaluation is still a bottleneck for developing robust perception models. In this paper, we present the ApolloScape dataset [1] and its applications for autonomous driving. Compared with existing public datasets from real scenes, e.g. KITTI [2] or Cityscapes [3], ApolloScape contains much large and richer labelling including holistic semantic dense point cloud for each site, stereo, per-pixel semantic labelling, lanemark labelling, instance segmentation, 3D car instance, high accurate location for every frame in various driving videos from multiple sites, cities and daytimes. For each task, it contains at lease 15x larger amount of images than SOTA datasets. To label such a complete dataset, we develop various tools and algorithms specified for each task to accelerate the labelling process, such as 3D-2D segment labeling tools, active labelling in videos etc. Depend on ApolloScape, we are able to develop algorithms jointly consider the learning and inference of multiple tasks. In this paper, we provide a sensor fusion scheme integrating camera videos, consumer-grade motion sensors (GPS/IMU), and a 3D semantic map in order to achieve robust self-localization and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving. We show that practically, sensor fusion and joint learning of multiple tasks are beneficial to achieve a more robust and accurate system. We expect our dataset and proposed relevant algorithms can support and motivate researchers for further development of multi-sensor fusion and multi-task learning in the field of computer vision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge