Tensor Component Analysis for Interpreting the Latent Space of GANs
Paper and Code
Nov 23, 2021
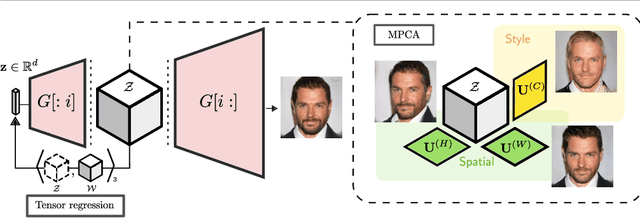
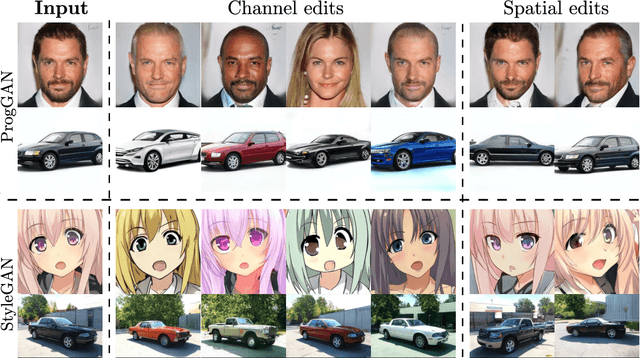

This paper addresses the problem of finding interpretable directions in the latent space of pre-trained Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to facilitate controllable image synthesis. Such interpretable directions correspond to transformations that can affect both the style and geometry of the synthetic images. However, existing approaches that utilise linear techniques to find these transformations often fail to provide an intuitive way to separate these two sources of variation. To address this, we propose to a) perform a multilinear decomposition of the tensor of intermediate representations, and b) use a tensor-based regression to map directions found using this decomposition to the latent space. Our scheme allows for both linear edits corresponding to the individual modes of the tensor, and non-linear ones that model the multiplicative interactions between them. We show experimentally that we can utilise the former to better separate style- from geometry-based transformations, and the latter to generate an extended set of possible transformations in comparison to prior works. We demonstrate our approach's efficacy both quantitatively and qualitatively compared to the current state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge