Synthesizing Mixed-type Electronic Health Records using Diffusion Models
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2023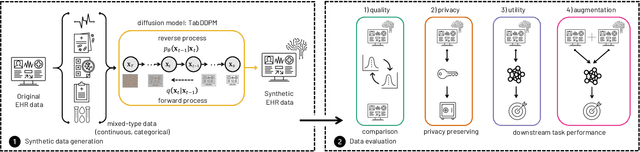
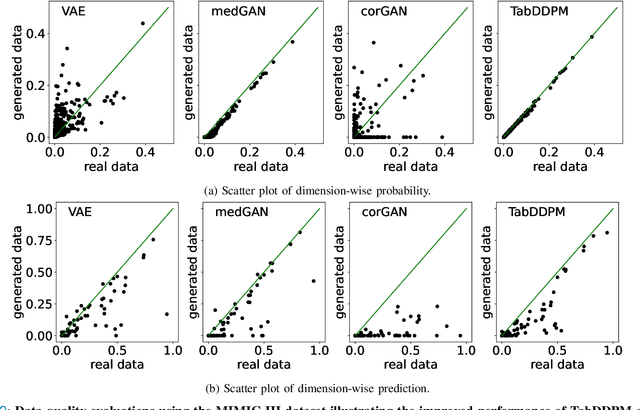
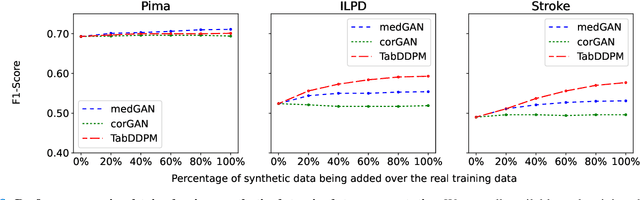
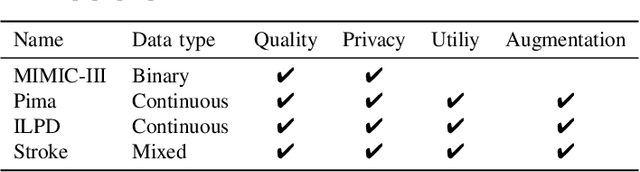
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) contain sensitive patient information, which presents privacy concerns when sharing such data. Synthetic data generation is a promising solution to mitigate these risks, often relying on deep generative models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). However, recent studies have shown that diffusion models offer several advantages over GANs, such as generation of more realistic synthetic data and stable training in generating data modalities, including image, text, and sound. In this work, we investigate the potential of diffusion models for generating realistic mixed-type tabular EHRs, comparing TabDDPM model with existing methods on four datasets in terms of data quality, utility, privacy, and augmentation. Our experiments demonstrate that TabDDPM outperforms the state-of-the-art models across all evaluation metrics, except for privacy, which confirms the trade-off between privacy and utility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge