Synonym Knowledge Enhanced Reader for Chinese Idiom Reading Comprehension
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2020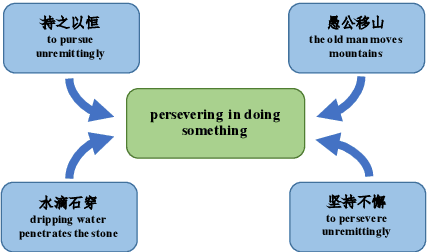
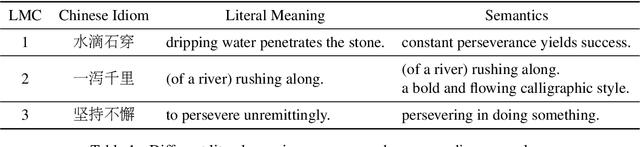
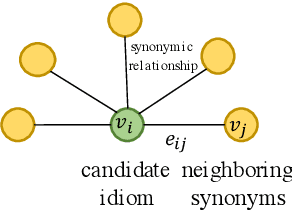
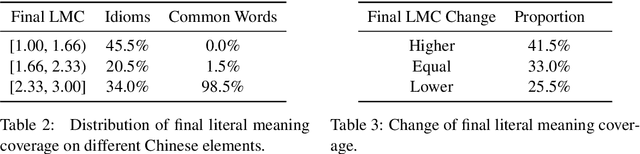
Machine reading comprehension (MRC) is the task that asks a machine to answer questions based on a given context. For Chinese MRC, due to the non-literal and non-compositional semantic characteristics, Chinese idioms pose unique challenges for machines to understand. Previous studies tend to treat idioms separately without fully exploiting the relationship among them. In this paper, we first define the concept of literal meaning coverage to measure the consistency between semantics and literal meanings for Chinese idioms. With the definition, we prove that the literal meanings of many idioms are far from their semantics, and we also verify that the synonymic relationship can mitigate this inconsistency, which would be beneficial for idiom comprehension. Furthermore, to fully utilize the synonymic relationship, we propose the synonym knowledge enhanced reader. Specifically, for each idiom, we first construct a synonym graph according to the annotations from a high-quality synonym dictionary or the cosine similarity between the pre-trained idiom embeddings and then incorporate the graph attention network and gate mechanism to encode the graph. Experimental results on ChID, a large-scale Chinese idiom reading comprehension dataset, show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge