Student-Teacher Learning from Clean Inputs to Noisy Inputs
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2021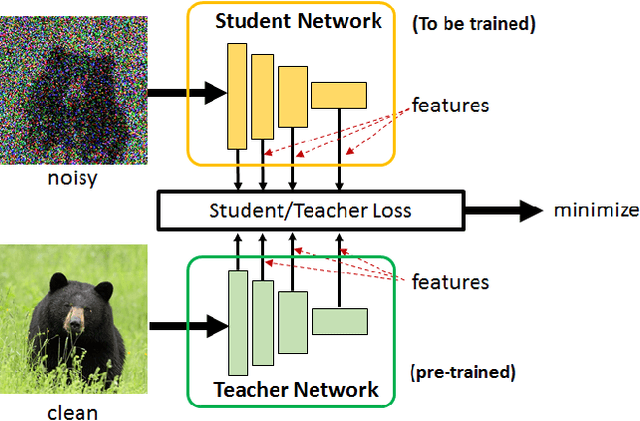

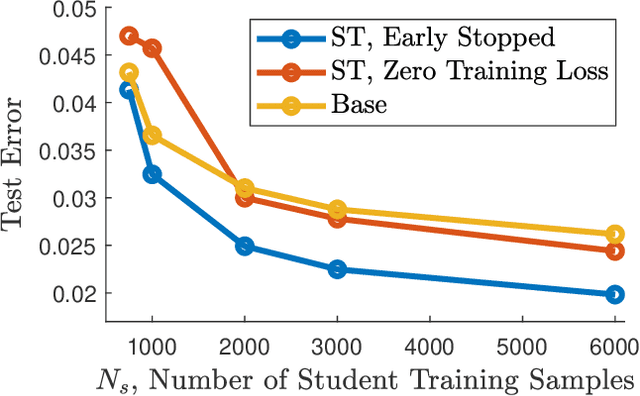
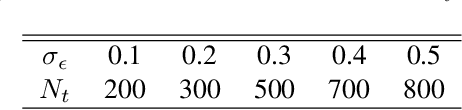
Feature-based student-teacher learning, a training method that encourages the student's hidden features to mimic those of the teacher network, is empirically successful in transferring the knowledge from a pre-trained teacher network to the student network. Furthermore, recent empirical results demonstrate that, the teacher's features can boost the student network's generalization even when the student's input sample is corrupted by noise. However, there is a lack of theoretical insights into why and when this method of transferring knowledge can be successful between such heterogeneous tasks. We analyze this method theoretically using deep linear networks, and experimentally using nonlinear networks. We identify three vital factors to the success of the method: (1) whether the student is trained to zero training loss; (2) how knowledgeable the teacher is on the clean-input problem; (3) how the teacher decomposes its knowledge in its hidden features. Lack of proper control in any of the three factors leads to failure of the student-teacher learning method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge