Structured Deep Kernel Networks for Data-Driven Closure Terms of Turbulent Flows
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2021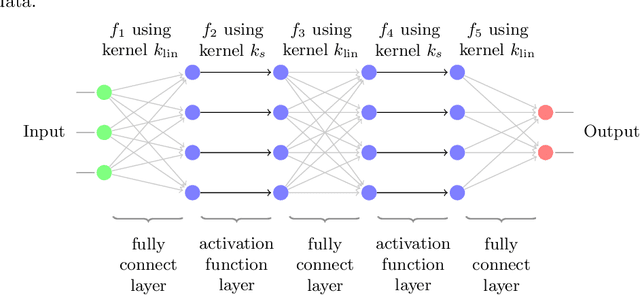
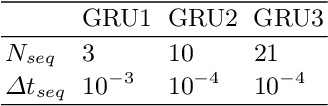
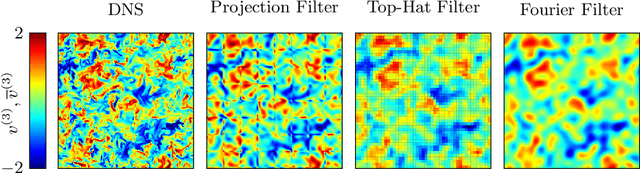
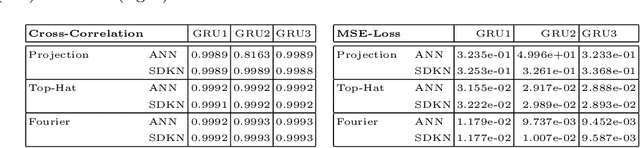
Standard kernel methods for machine learning usually struggle when dealing with large datasets. We review a recently introduced Structured Deep Kernel Network (SDKN) approach that is capable of dealing with high-dimensional and huge datasets - and enjoys typical standard machine learning approximation properties. We extend the SDKN to combine it with standard machine learning modules and compare it with Neural Networks on the scientific challenge of data-driven prediction of closure terms of turbulent flows. We show experimentally that the SDKNs are capable of dealing with large datasets and achieve near-perfect accuracy on the given application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge