Stochastic Region Pooling: Make Attention More Expressive
Paper and Code
Apr 22, 2019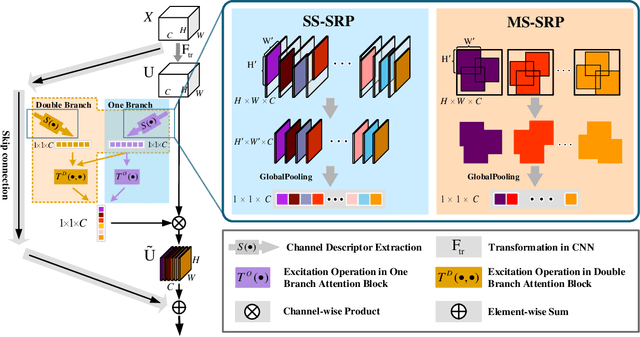
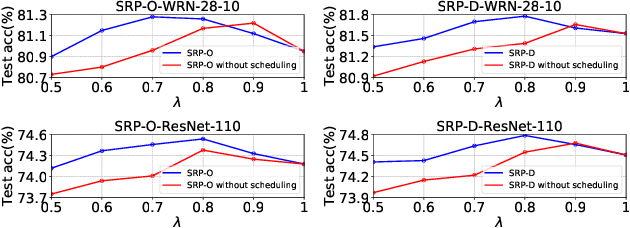
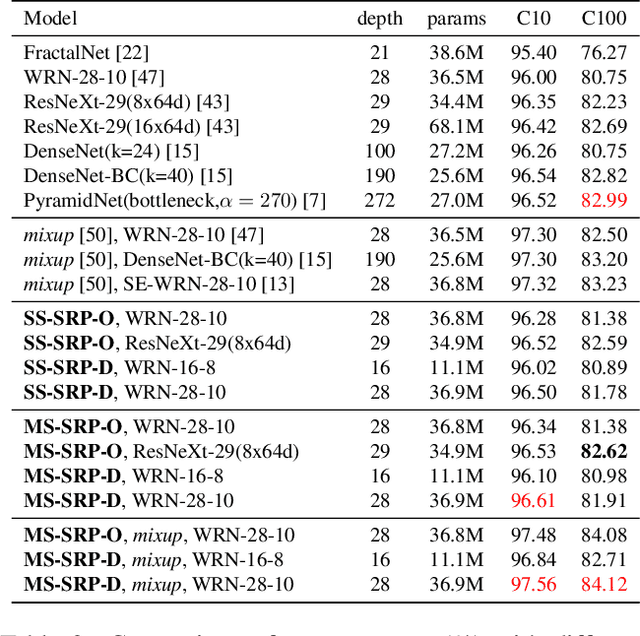
Global Average Pooling (GAP) is used by default on the channel-wise attention mechanism to extract channel descriptors. However, the simple global aggregation method of GAP is easy to make the channel descriptors have homogeneity, which weakens the detail distinction between feature maps, thus affecting the performance of the attention mechanism. In this work, we propose a novel method for channel-wise attention network, called Stochastic Region Pooling (SRP), which makes the channel descriptors more representative and diversity by encouraging the feature map to have more or wider important feature responses. Also, SRP is the general method for the attention mechanisms without any additional parameters or computation. It can be widely applied to attention networks without modifying the network structure. Experimental results on image recognition datasets including CIAFR-10/100, ImageNet and three Fine-grained datasets (CUB-200-2011, Stanford Cars and Stanford Dogs) show that SRP brings the significant improvements of the performance over efficient CNNs and achieves the state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge