Stationary Multi-source AI-powered Real-time Tomography for Dynamic Cardiac Imaging
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2021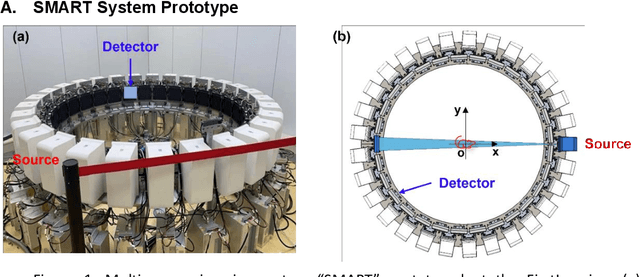
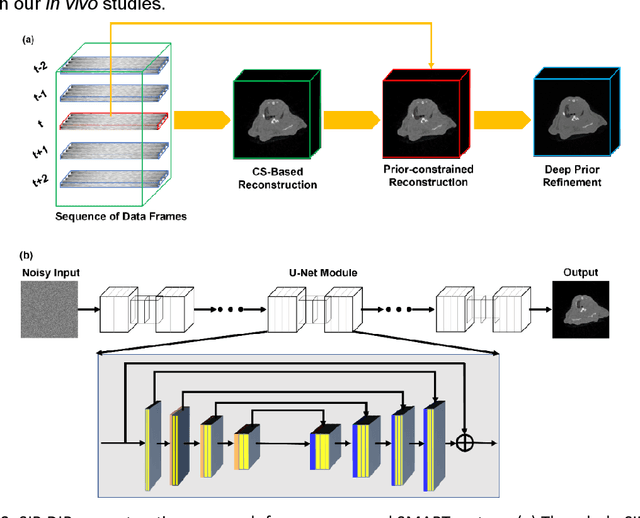
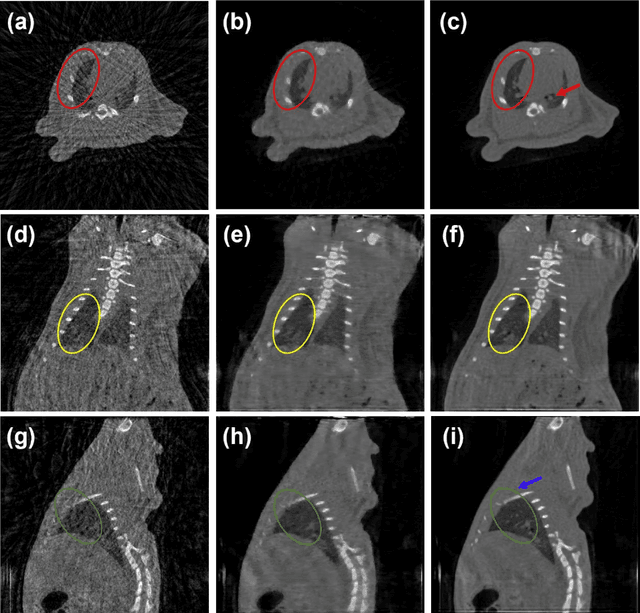
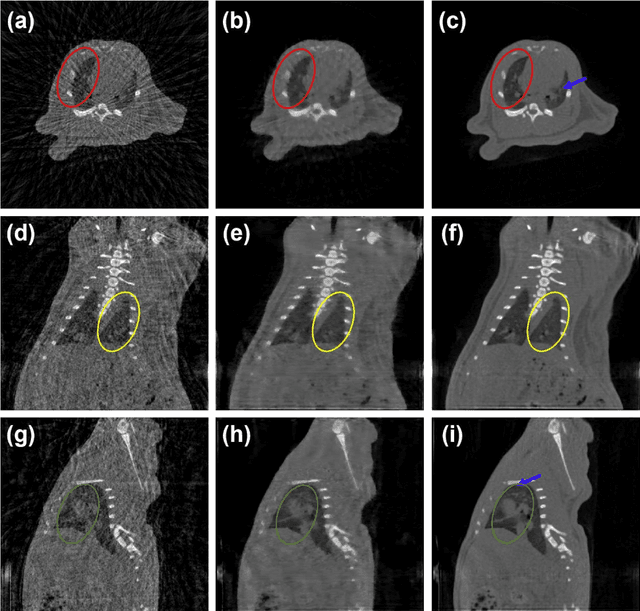
A first stationary multi-source computed tomography (CT) system is prototyped for preclinical imaging to achieve real-time temporal resolution for dynamic cardiac imaging. This unique is featured by 29 source-detector pairs fixed on a circular track for each detector to collect x-ray signals only from the opposite x-ray source. The new system architecture potentially leads to a major improvement in temporal resolution. To demonstrate the feasibility of this Stationary Multi-source AI-based Real-time Tomography (SMART) system, we develop a novel reconstruction scheme integrating both sparsified image prior (SIP) and deep image prior (DIP), which is referred to as the SIP-DIP network. Then, the SIP-DIP network for cardiac imaging is evaluated on preclinical cardiac datasets of alive rats. The reconstructed image volumes demonstrate the feasibility of the SMART system and the SIP-DIP network and the merits over other reconstruction methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge