SQATIN: Supervised Instruction Tuning Meets Question Answering for Improved Dialogue NLU
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2023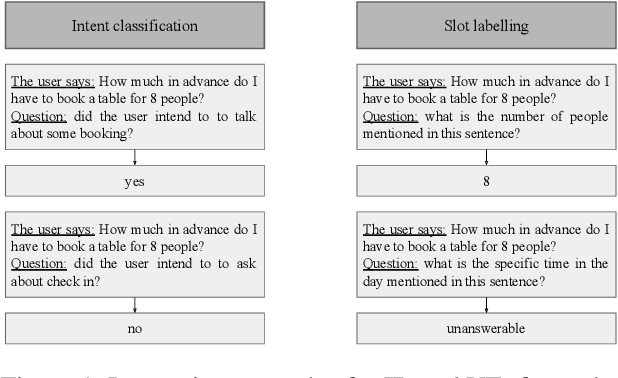
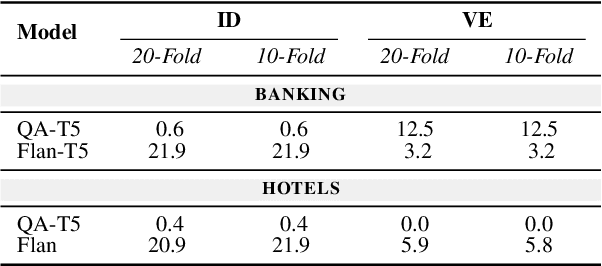
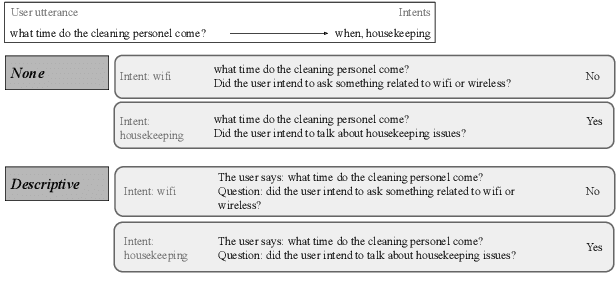
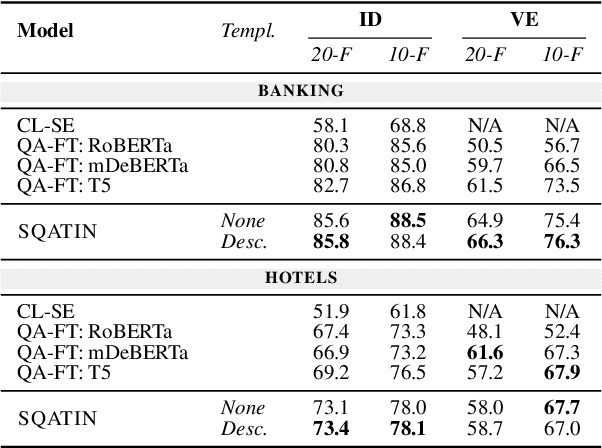
Task-oriented dialogue (ToD) systems help users execute well-defined tasks across a variety of domains (e.g., $\textit{flight booking}$ or $\textit{food ordering}$), with their Natural Language Understanding (NLU) components being dedicated to the analysis of user utterances, predicting users' intents ($\textit{Intent Detection}$, ID) and extracting values for informational slots ($\textit{Value Extraction}$, VE). In most domains, labelled NLU data is scarce, making sample-efficient learning -- enabled with effective transfer paradigms -- paramount. In this work, we introduce SQATIN, a new framework for dialog NLU based on (i) instruction tuning and (ii) question-answering-based formulation of ID and VE tasks. According to the evaluation on established NLU benchmarks, SQATIN sets the new state of the art in dialogue NLU, substantially surpassing the performance of current models based on standard fine-tuning objectives in both in-domain training and cross-domain transfer. SQATIN yields particularly large performance gains in cross-domain transfer, owing to the fact that our QA-based instruction tuning leverages similarities between natural language descriptions of classes (i.e., slots and intents) across domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge