SPOTS: Stable Placement of Objects with Reasoning in Semi-Autonomous Teleoperation Systems
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2023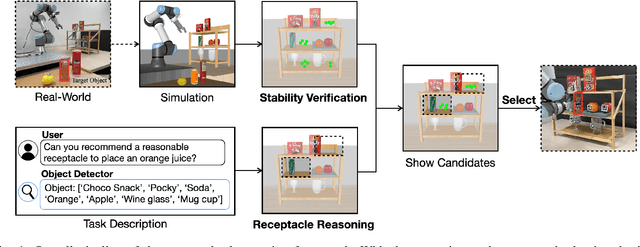
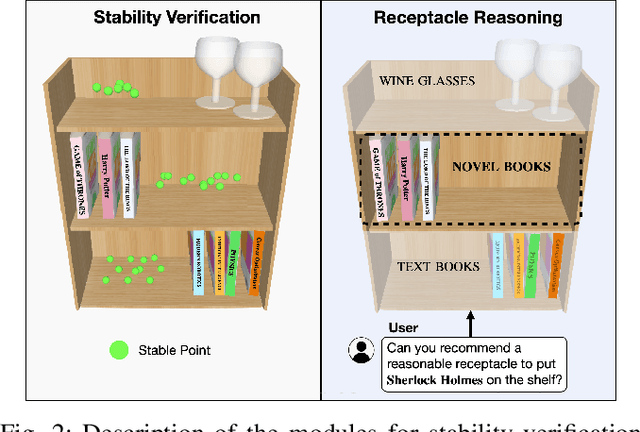
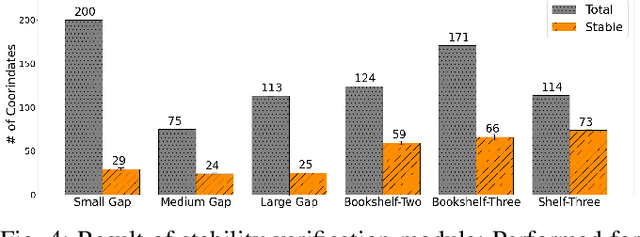
Pick-and-place is one of the fundamental tasks in robotics research. However, the attention has been mostly focused on the ``pick'' task, leaving the ``place'' task relatively unexplored. In this paper, we address the problem of placing objects in the context of a teleoperation framework. Particularly, we focus on two aspects of the place task: stability robustness and contextual reasonableness of object placements. Our proposed method combines simulation-driven physical stability verification via real-to-sim and the semantic reasoning capability of large language models. In other words, given place context information (e.g., user preferences, object to place, and current scene information), our proposed method outputs a probability distribution over the possible placement candidates, considering the robustness and reasonableness of the place task. Our proposed method is extensively evaluated in two simulation and one real world environments and we show that our method can greatly increase the physical plausibility of the placement as well as contextual soundness while considering user preferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge