SPATL: Salient Parameter Aggregation and Transfer Learning for Heterogeneous Clients in Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2021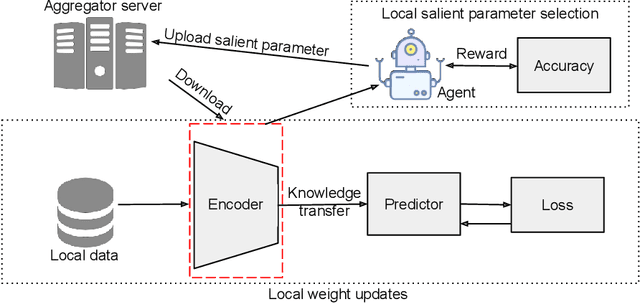
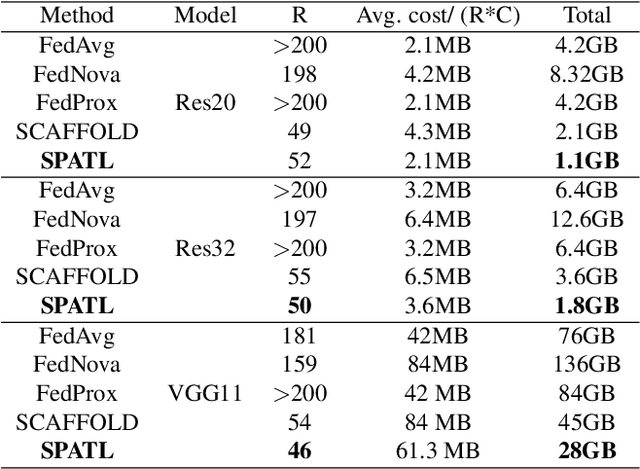
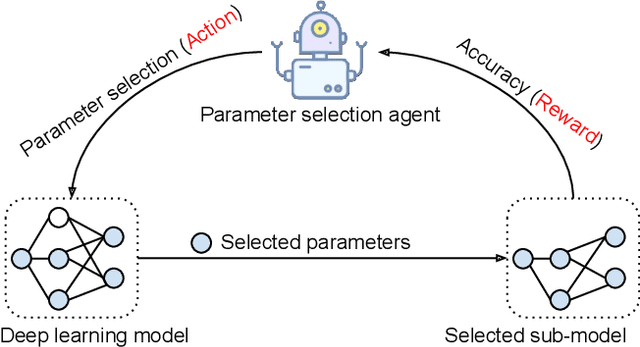
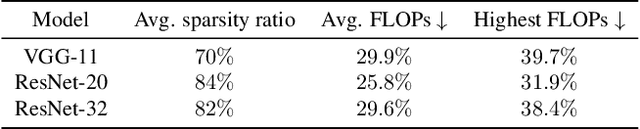
Efficient federated learning is one of the key challenges for training and deploying AI models on edge devices. However, maintaining data privacy in federated learning raises several challenges including data heterogeneity, expensive communication cost, and limited resources. In this paper, we address the above issues by (a) introducing a salient parameter selection agent based on deep reinforcement learning on local clients, and aggregating the selected salient parameters on the central server, and (b) splitting a normal deep learning model~(e.g., CNNs) as a shared encoder and a local predictor, and training the shared encoder through federated learning while transferring its knowledge to Non-IID clients by the local customized predictor. The proposed method (a) significantly reduces the communication overhead of federated learning and accelerates the model inference, while method (b) addresses the data heterogeneity issue in federated learning. Additionally, we leverage the gradient control mechanism to correct the gradient heterogeneity among clients. This makes the training process more stable and converge faster. The experiments show our approach yields a stable training process and achieves notable results compared with the state-of-the-art methods. Our approach significantly reduces the communication cost by up to 108 GB when training VGG-11, and needed $7.6 \times$ less communication overhead when training ResNet-20, while accelerating the local inference by reducing up to $39.7\%$ FLOPs on VGG-11.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge