Sparse hierarchical representation learning on molecular graphs
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2019
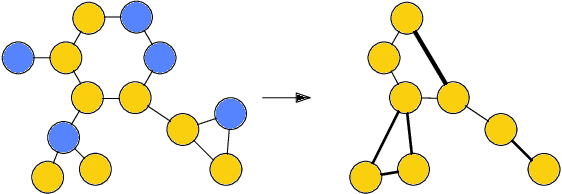

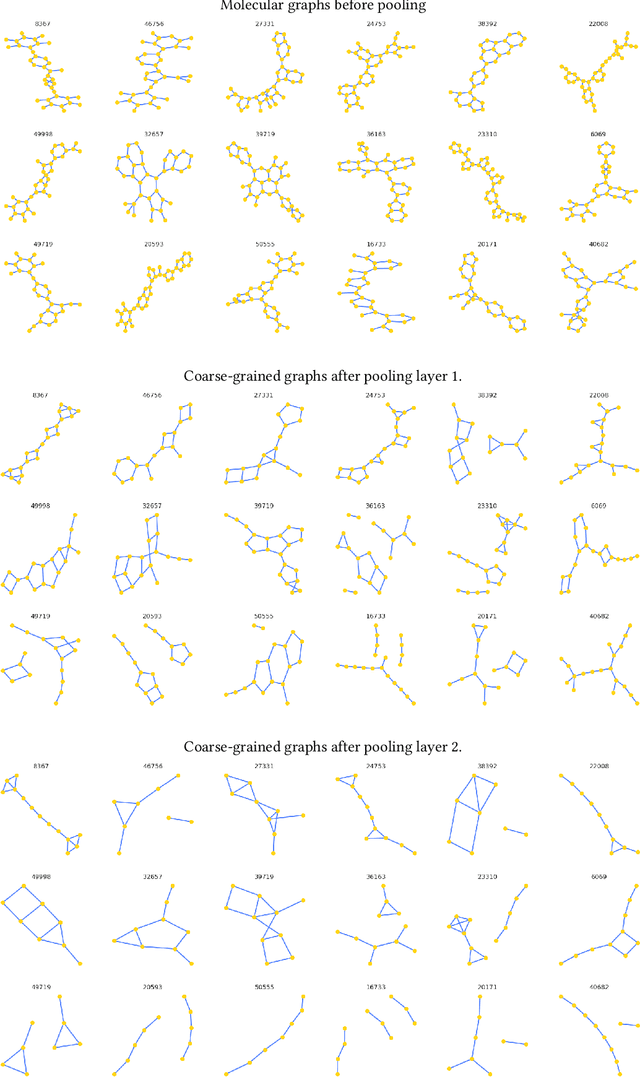
Architectures for sparse hierarchical representation learning have recently been proposed for graph-structured data, but so far assume the absence of edge features in the graph. We close this gap and propose a method to pool graphs with edge features, inspired by the hierarchical nature of chemistry. In particular, we introduce two types of pooling layers compatible with an edge-feature graph-convolutional architecture and investigate their performance for molecules relevant to drug discovery on a set of two classification and two regression benchmark datasets of MoleculeNet. We find that our models significantly outperform previous benchmarks on three of the datasets and reach state-of-the-art results on the fourth benchmark, with pooling improving performance for three out of four tasks, keeping performance stable on the fourth task, and generally speeding up the training process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge