Soft Robots Modeling: a Literature Unwinding
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2021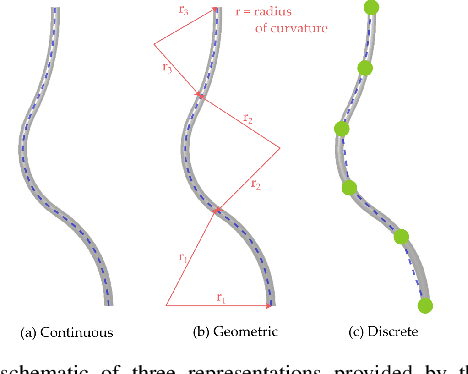

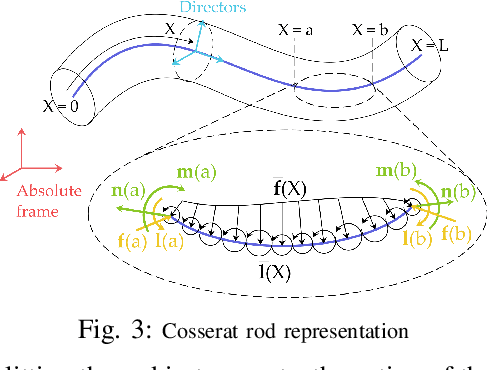
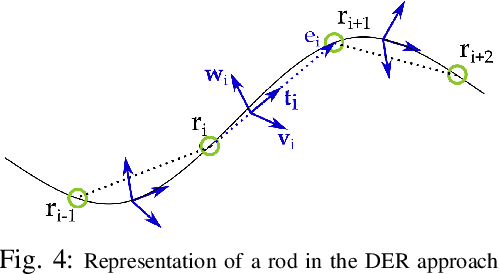
The robotics community has seen an exponential growth in the level of complexity of the theoretical tools presented for the modeling of soft robotics devices. Different solutions have been presented to overcome the difficulties related to the modeling of soft robots, often leveraging on other scientific disciplines, such as continuum mechanics and computer graphics. These theoretical foundations are often taken for granted and this lead to an intricate literature that, consequently, has never been the subject of a complete review. Withing this scenario, the objective of the presented paper is twofold. The common theoretical roots that relate the different families of modeling techniques are highlighted, employing a unifying language that ease the analysis of their main connections and differences. Thus, the listing of the approaches naturally follows and a complete, untangled, review of the main works on the field is finally provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge