SMT vs NMT: A Comparison over Hindi & Bengali Simple Sentences
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2018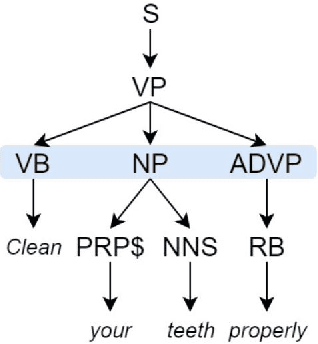
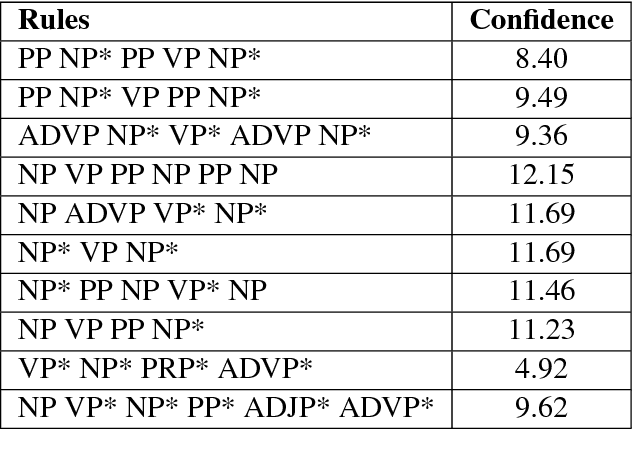
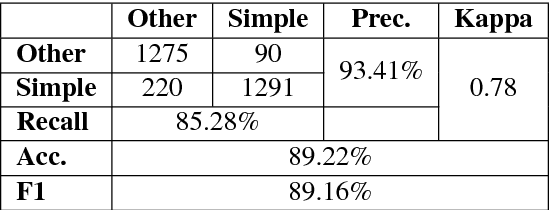
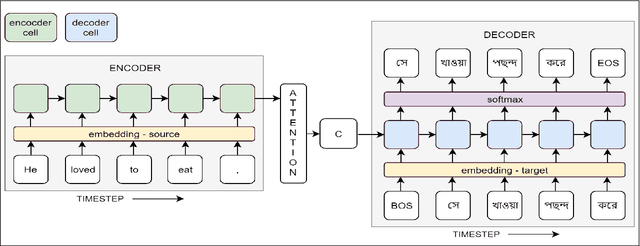
In the present article, we identified the qualitative differences between Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) and Neural Machine Translation (NMT) outputs. We have tried to answer two important questions: 1. Does NMT perform equivalently well with respect to SMT and 2. Does it add extra flavor in improving the quality of MT output by employing simple sentences as training units. In order to obtain insights, we have developed three core models viz., SMT model based on Moses toolkit, followed by character and word level NMT models. All of the systems use English-Hindi and English-Bengali language pairs containing simple sentences as well as sentences of other complexity. In order to preserve the translations semantics with respect to the target words of a sentence, we have employed soft-attention into our word level NMT model. We have further evaluated all the systems with respect to the scenarios where they succeed and fail. Finally, the quality of translation has been validated using BLEU and TER metrics along with manual parameters like fluency, adequacy etc. We observed that NMT outperforms SMT in case of simple sentences whereas SMT outperforms in case of all types of sentence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge