SiamAF: Learning Shared Information from ECG and PPG Signals for Robust Atrial Fibrillation Detection
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2023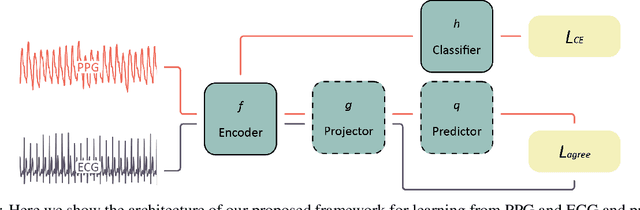
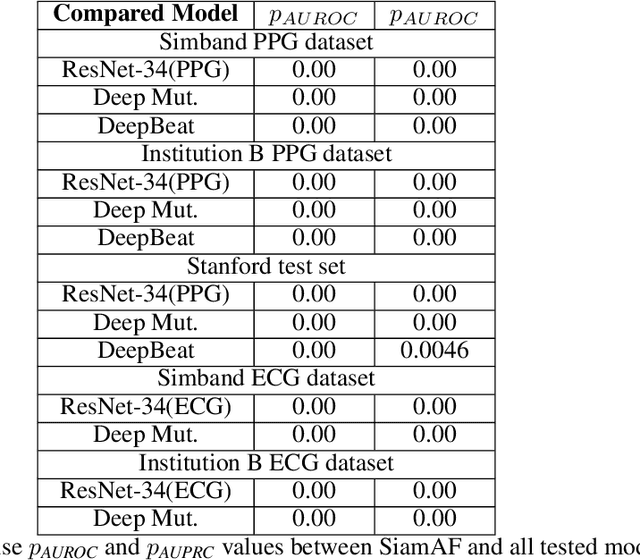
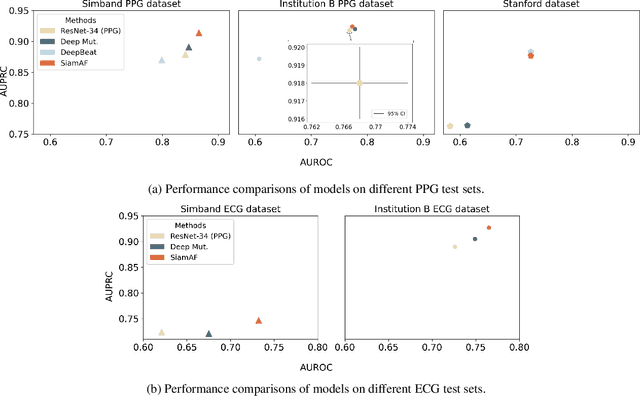
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of cardiac arrhythmia. It is associated with an increased risk of stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular complications, but can be clinically silent. Passive AF monitoring with wearables may help reduce adverse clinical outcomes related to AF. Detecting AF in noisy wearable data poses a significant challenge, leading to the emergence of various deep learning techniques. Previous deep learning models learn from a single modality, either electrocardiogram (ECG) or photoplethysmography (PPG) signals. However, deep learning models often struggle to learn generalizable features and rely on features that are more susceptible to corruption from noise, leading to sub-optimal performances in certain scenarios, especially with low-quality signals. Given the increasing availability of ECG and PPG signal pairs from wearables and bedside monitors, we propose a new approach, SiamAF, leveraging a novel Siamese network architecture and joint learning loss function to learn shared information from both ECG and PPG signals. At inference time, the proposed model is able to predict AF from either PPG or ECG and outperforms baseline methods on three external test sets. It learns medically relevant features as a result of our novel architecture design. The proposed model also achieves comparable performance to traditional learning regimes while requiring much fewer training labels, providing a potential approach to reduce future reliance on manual labeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge