Sentiment Analysis based Multi-person Multi-criteria Decision Making Methodology: Using Natural Language Processing and Deep Learning for Decision Aid
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2020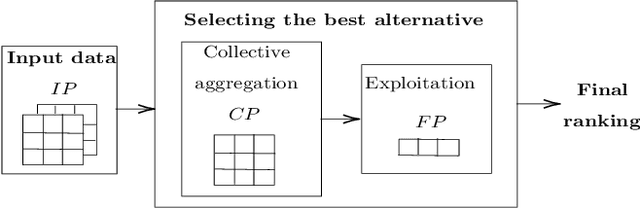
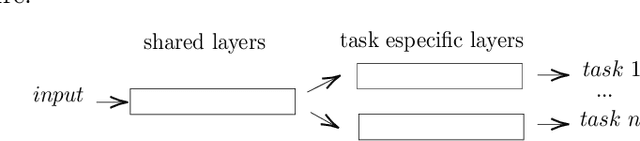

Decision making models are constrained by taking the expert evaluations with pre-defined numerical or linguistic terms. We claim that the use of sentiment analysis will allow decision making models to consider expert evaluations in natural language. Accordingly, we propose the Sentiment Analysis based Multi-person Multi-criteria Decision Making (SA-MpMcDM) methodology, which builds the expert evaluations from their natural language reviews, and even from their numerical ratings if they are available. The SA-MpMcDM methodology incorporates an end-to-end multi-task deep learning model for aspect based sentiment analysis, named DMuABSA model, able to identify the aspect categories mentioned in an expert review, and to distill their opinions and criteria. The individual expert evaluations are aggregated via a criteria weighting through the attention of the experts. We evaluate the methodology in a restaurant decision problem, hence we build the TripR-2020 dataset of restaurant reviews, which we manually annotate and release. We analyze the SA-MpMcDM methodology in different scenarios using and not using natural language and numerical evaluations. The analysis shows that the combination of both sources of information results in a higher quality preference vector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge