Semi-Supervised Fine-Tuning of Vision Foundation Models with Content-Style Decomposition
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2024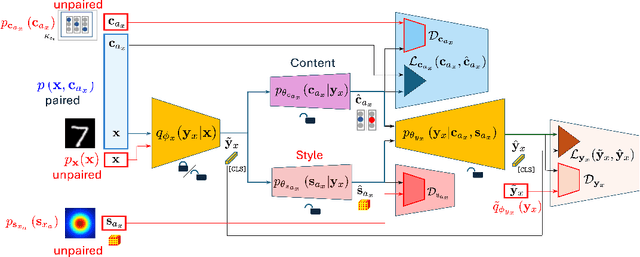



In this paper, we present a semi-supervised fine-tuning approach designed to improve the performance of foundation models on downstream tasks with limited labeled data. By leveraging content-style decomposition within an information-theoretic framework, our method enhances the latent representations of pre-trained vision foundation models, aligning them more effectively with specific task objectives and addressing the problem of distribution shift. We evaluate our approach on multiple datasets, including MNIST, its augmented variations (with yellow and white stripes), CIFAR-10, SVHN, and GalaxyMNIST. The experiments show improvements over purely supervised baselines, particularly in low-labeled data regimes, across both frozen and trainable backbones for the majority of the tested datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge