Self-supervised Adaptive Weighting for Cooperative Perception in V2V Communications
Paper and Code
Dec 16, 2023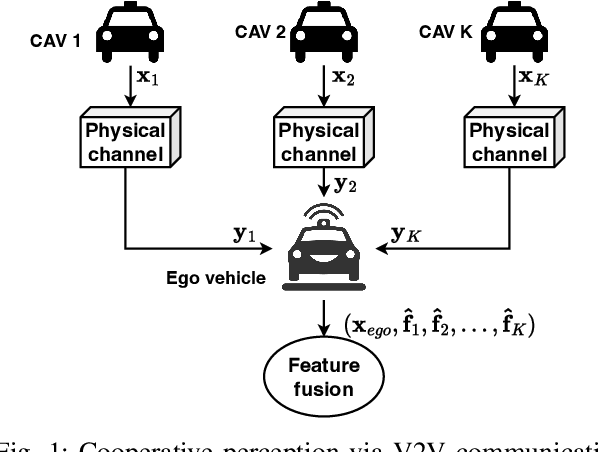
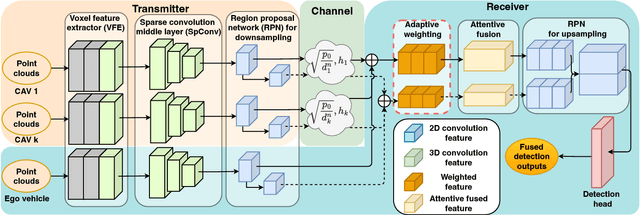
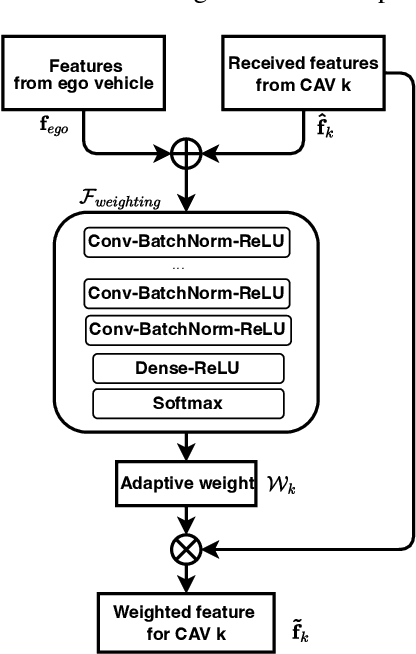
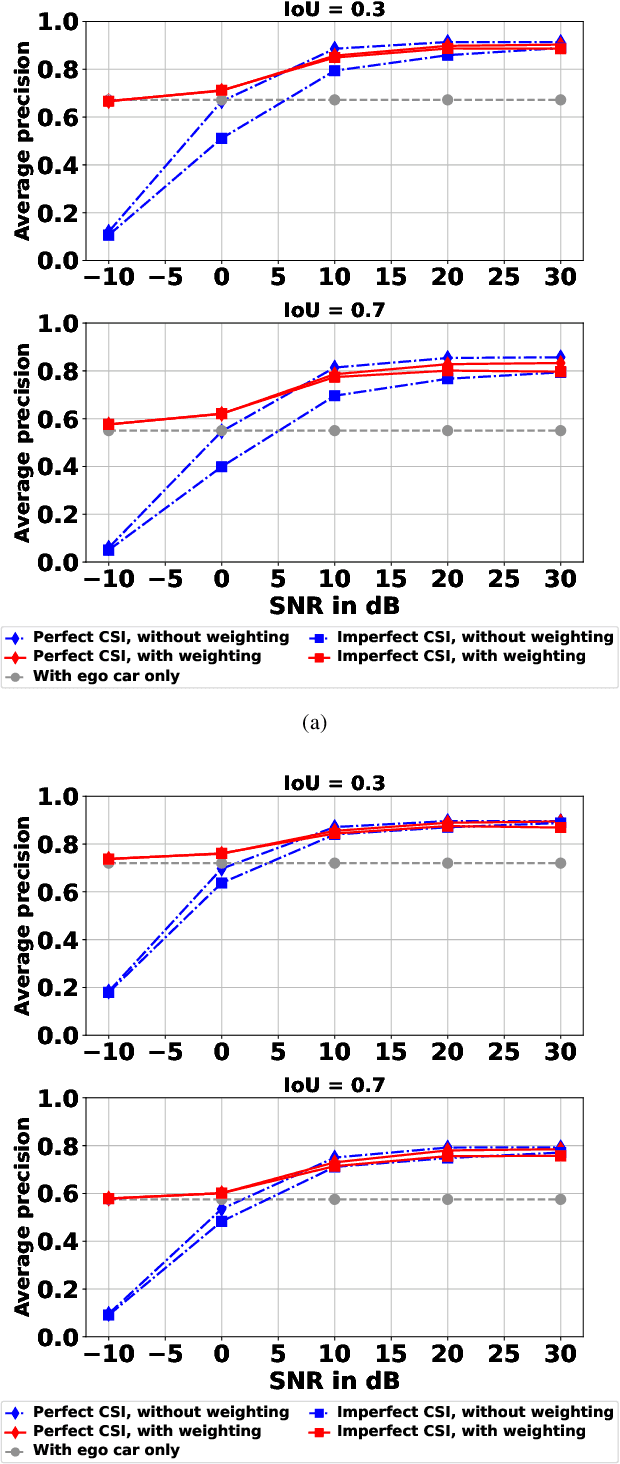
Perception of the driving environment is critical for collision avoidance and route planning to ensure driving safety. Cooperative perception has been widely studied as an effective approach to addressing the shortcomings of single-vehicle perception. However, the practical limitations of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications have not been adequately investigated. In particular, current cooperative fusion models rely on supervised models and do not address dynamic performance degradation caused by arbitrary channel impairments. In this paper, a self-supervised adaptive weighting model is proposed for intermediate fusion to mitigate the adverse effects of channel distortion. The performance of cooperative perception is investigated in different system settings. Rician fading and imperfect channel state information (CSI) are also considered. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed adaptive weighting algorithm significantly outperforms the benchmarks without weighting. Visualization examples validate that the proposed weighting algorithm can flexibly adapt to various channel conditions. Moreover, the adaptive weighting algorithm demonstrates good generalization to untrained channels and test datasets from different domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge