Self-slimmed Vision Transformer
Paper and Code
Nov 24, 2021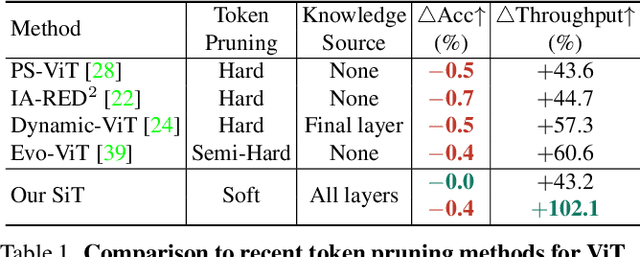
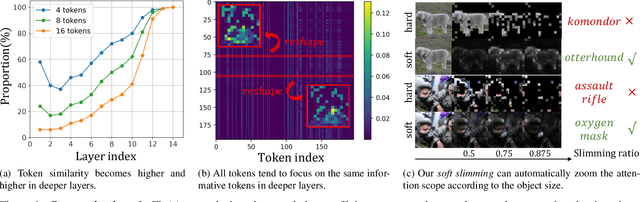
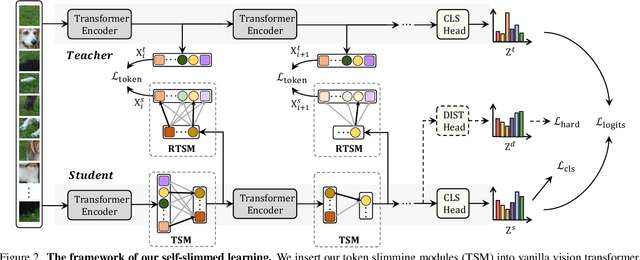
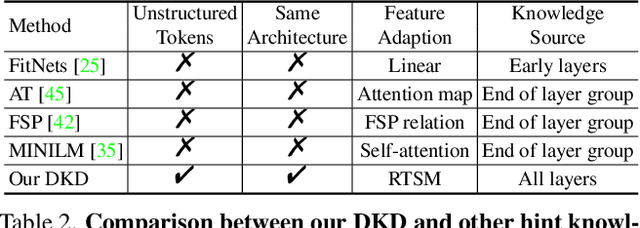
Vision transformers (ViTs) have become the popular structures and outperformed convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on various vision tasks. However, such powerful transformers bring a huge computation burden. And the essential barrier behind this is the exhausting token-to-token comparison. To alleviate this, we delve deeply into the model properties of ViT and observe that ViTs exhibit sparse attention with high token similarity. This intuitively introduces us a feasible structure-agnostic dimension, token number, to reduce the computational cost. Based on this exploration, we propose a generic self-slimmed learning approach for vanilla ViTs, namely SiT. Specifically, we first design a novel Token Slimming Module (TSM), which can boost the inference efficiency of ViTs by dynamic token aggregation. Different from the token hard dropping, our TSM softly integrates redundant tokens into fewer informative ones, which can dynamically zoom visual attention without cutting off discriminative token relations in the images. Furthermore, we introduce a concise Dense Knowledge Distillation (DKD) framework, which densely transfers unorganized token information in a flexible auto-encoder manner. Due to the similar structure between teacher and student, our framework can effectively leverage structure knowledge for better convergence. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments to evaluate our SiT. It demonstrates that our method can speed up ViTs by 1.7x with negligible accuracy drop, and even speed up ViTs by 3.6x while maintaining 97% of their performance. Surprisingly, by simply arming LV-ViT with our SiT, we achieve new state-of-the-art performance on ImageNet, surpassing all the CNNs and ViTs in the recent literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge