See More Than Once -- Kernel-Sharing Atrous Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
Sep 09, 2019
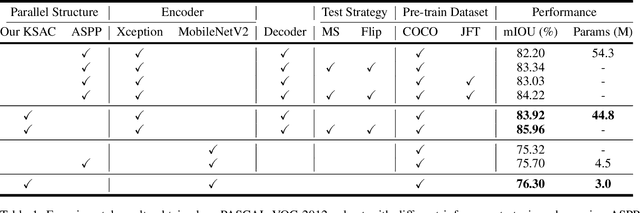
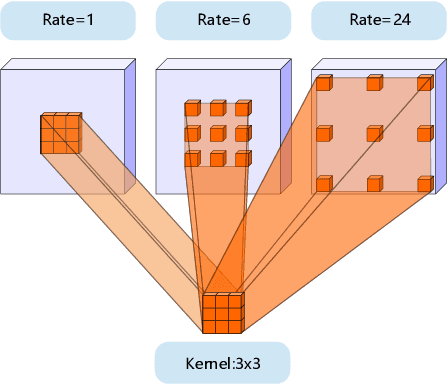
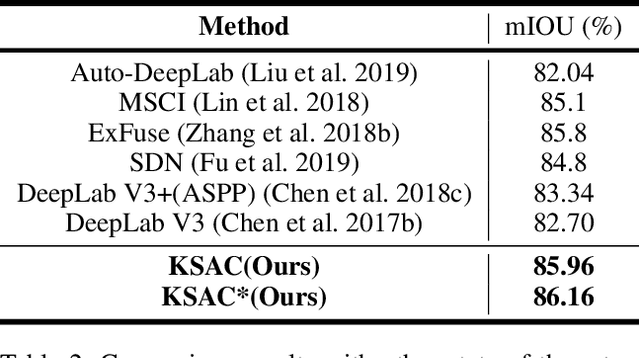
The state-of-the-art semantic segmentation solutions usually leverage different receptive fields via multiple parallel branches to handle objects with different sizes. However, employing separate kernels for individual branches degrades the generalization and representation abilities of the network, and the amount of parameters increases by the times of the number of branches. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel network structure namely Kernel-Sharing Atrous Convolution (KSAC), where branches of different receptive fields share the same kernel, i.e., let a single kernel `see' the input feature maps more than once with different receptive fields, to facilitate communication among branches and perform `feature augmentation' inside the network. Experiments conducted on the benchmark VOC 2012 dataset show that the proposed sharing strategy can not only boost network's generalization and representation abilities but also reduce the model complexity significantly. Specifically, when compared with DeepLabV3+ equipped with MobileNetv2 backbone, 33% parameters are reduced together with an mIOU improvement of 0.6%. When Xception is used as the backbone, the mIOU is elevated from 83.34% to 85.96% with about 10M parameters saved. In addition, different from the widely used ASPP structure, our proposed KSAC is able to further improve the mIOU by taking benefit of wider context with larger atrous rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge