SECRET: Semantically Enhanced Classification of Real-world Tasks
Paper and Code
May 29, 2019
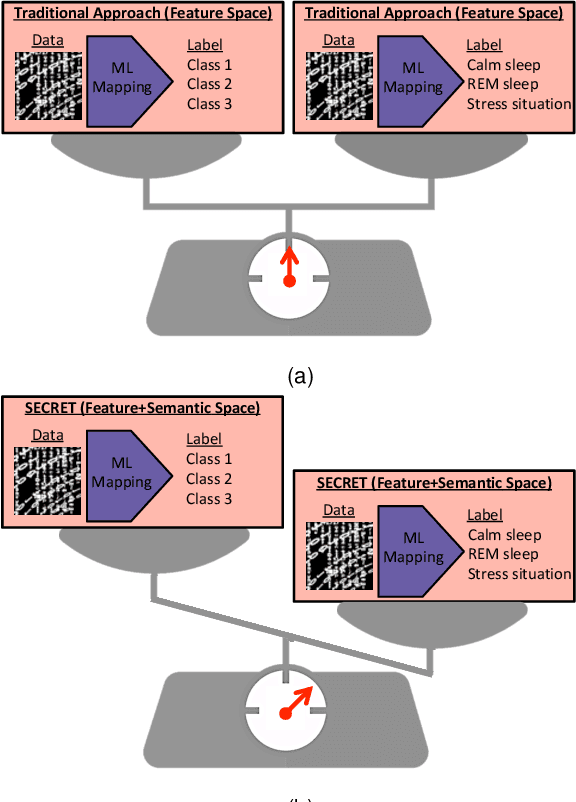
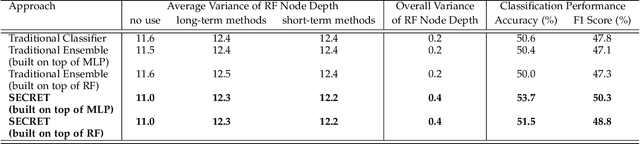
Supervised machine learning (ML) algorithms are aimed at maximizing classification performance under available energy and storage constraints. They try to map the training data to the corresponding labels while ensuring generalizability to unseen data. However, they do not integrate meaning-based relationships among labels in the decision process. On the other hand, natural language processing (NLP) algorithms emphasize the importance of semantic information. In this paper, we synthesize the complementary advantages of supervised ML and natural language processing algorithms into one method that we refer to as SECRET (Semantically Enhanced Classification of REal-world Tasks). SECRET performs classifications by fusing the semantic information of the labels with the available data: it combines the feature space of the supervised algorithms with the semantic space of the NLP algorithms and predicts labels based on this joint space. Experimental results indicate that, compared to traditional supervised learning, SECRET achieves up to 13.9% accuracy and 13.5% F1 score improvements. Moreover, compared to ensemble methods, SECRET achieves up to 12.6% accuracy and 13.8% F1 score improvements. This points to a new research direction for supervised classification by incorporating semantic information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge