SCAP: Transductive Test-Time Adaptation via Supportive Clique-based Attribute Prompting
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2025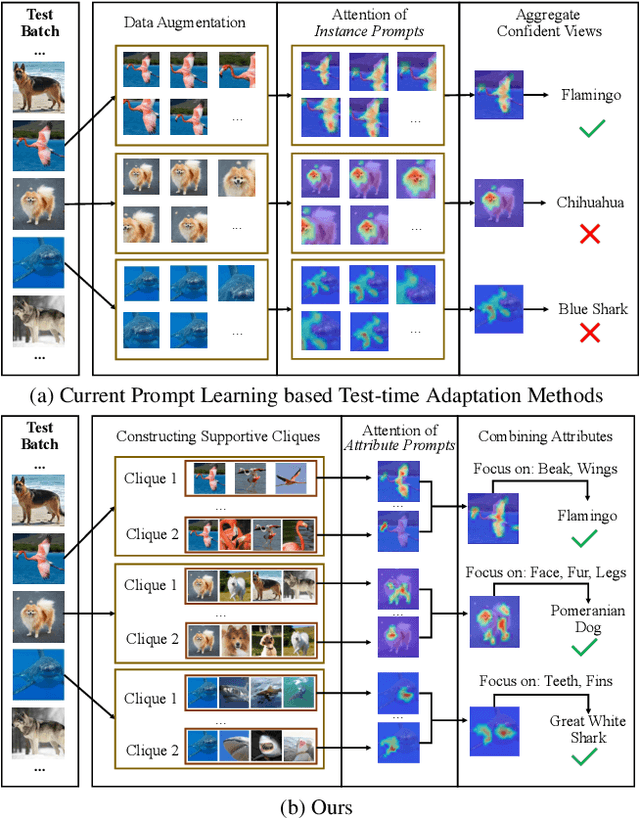
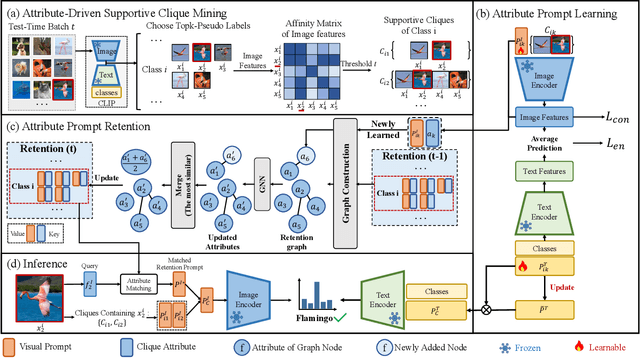
Vision-language models (VLMs) encounter considerable challenges when adapting to domain shifts stemming from changes in data distribution. Test-time adaptation (TTA) has emerged as a promising approach to enhance VLM performance under such conditions. In practice, test data often arrives in batches, leading to increasing interest in the transductive TTA setting. However, existing TTA methods primarily focus on individual test samples, overlooking crucial cross-sample correlations within a batch. While recent ViT-based TTA methods have introduced batch-level adaptation, they remain suboptimal for VLMs due to inadequate integration of the text modality. To address these limitations, we propose a novel transductive TTA framework, Supportive Clique-based Attribute Prompting (SCAP), which effectively combines visual and textual information to enhance adaptation by generating fine-grained attribute prompts across test batches. SCAP first forms supportive cliques of test samples in an unsupervised manner based on visual similarity and learns an attribute prompt for each clique, capturing shared attributes critical for adaptation. For each test sample, SCAP aggregates attribute prompts from its associated cliques, providing enriched contextual information. To ensure adaptability over time, we incorporate a retention module that dynamically updates attribute prompts and their associated attributes as new data arrives. Comprehensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that SCAP outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, significantly advancing VLM generalization under domain shifts. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhoujiahuan1991/CVPR2025-SCAP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge