S3Pool: Pooling with Stochastic Spatial Sampling
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2016
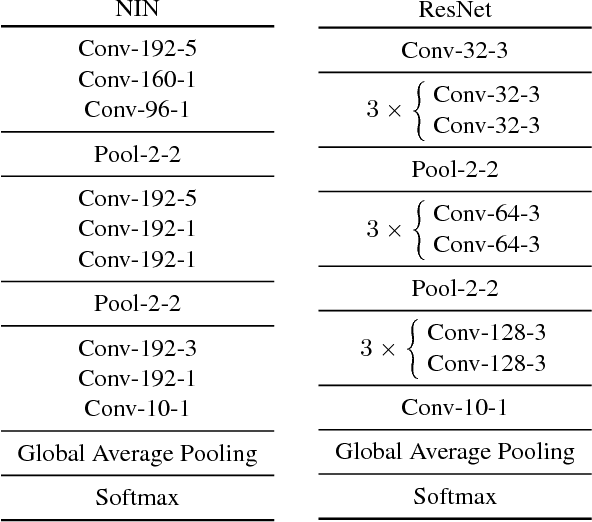
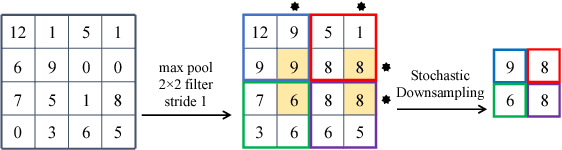
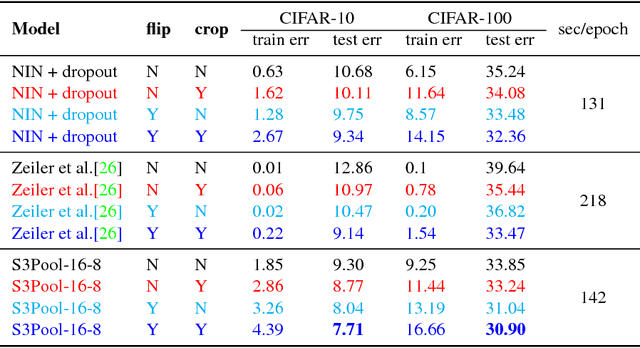
Feature pooling layers (e.g., max pooling) in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) serve the dual purpose of providing increasingly abstract representations as well as yielding computational savings in subsequent convolutional layers. We view the pooling operation in CNNs as a two-step procedure: first, a pooling window (e.g., $2\times 2$) slides over the feature map with stride one which leaves the spatial resolution intact, and second, downsampling is performed by selecting one pixel from each non-overlapping pooling window in an often uniform and deterministic (e.g., top-left) manner. Our starting point in this work is the observation that this regularly spaced downsampling arising from non-overlapping windows, although intuitive from a signal processing perspective (which has the goal of signal reconstruction), is not necessarily optimal for \emph{learning} (where the goal is to generalize). We study this aspect and propose a novel pooling strategy with stochastic spatial sampling (S3Pool), where the regular downsampling is replaced by a more general stochastic version. We observe that this general stochasticity acts as a strong regularizer, and can also be seen as doing implicit data augmentation by introducing distortions in the feature maps. We further introduce a mechanism to control the amount of distortion to suit different datasets and architectures. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we perform extensive experiments on several popular image classification benchmarks, observing excellent improvements over baseline models. Experimental code is available at https://github.com/Shuangfei/s3pool.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge