RS2G: Data-Driven Scene-Graph Extraction and Embedding for Robust Autonomous Perception and Scenario Understanding
Paper and Code
Apr 17, 2023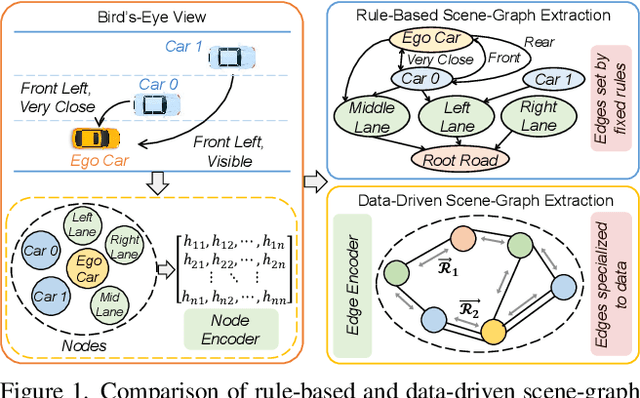
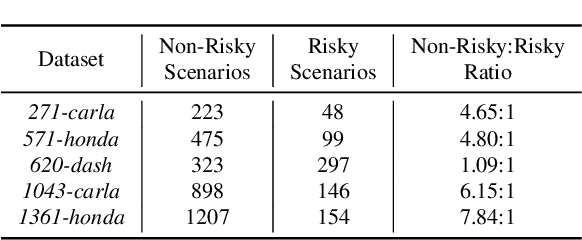
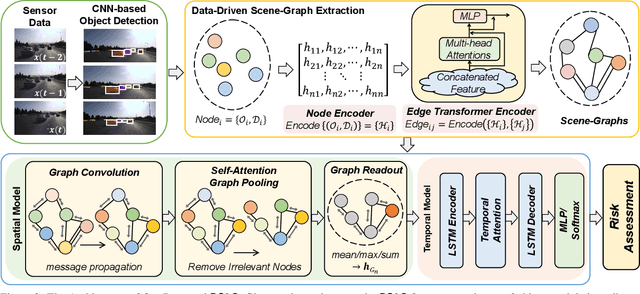
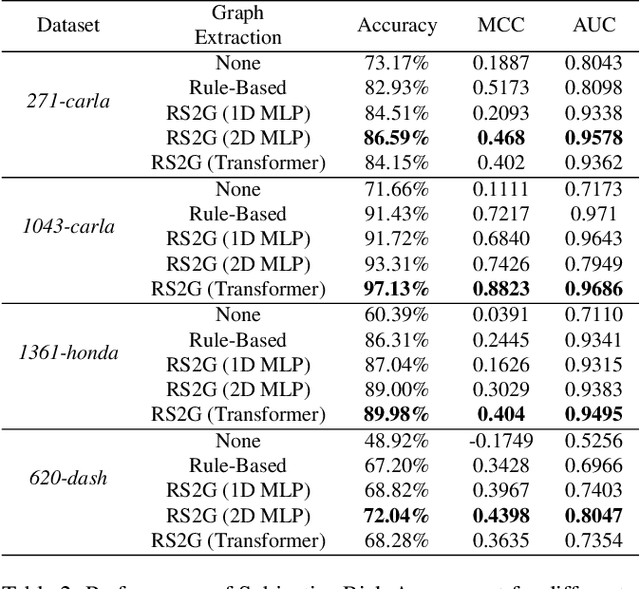
Human drivers naturally reason about interactions between road users to understand and safely navigate through traffic. Thus, developing autonomous vehicles necessitates the ability to mimic such knowledge and model interactions between road users to understand and navigate unpredictable, dynamic environments. However, since real-world scenarios often differ from training datasets, effectively modeling the behavior of various road users in an environment remains a significant research challenge. This reality necessitates models that generalize to a broad range of domains and explicitly model interactions between road users and the environment to improve scenario understanding. Graph learning methods address this problem by modeling interactions using graph representations of scenarios. However, existing methods cannot effectively transfer knowledge gained from the training domain to real-world scenarios. This constraint is caused by the domain-specific rules used for graph extraction that can vary in effectiveness across domains, limiting generalization ability. To address these limitations, we propose RoadScene2Graph (RS2G): a data-driven graph extraction and modeling approach that learns to extract the best graph representation of a road scene for solving autonomous scene understanding tasks. We show that RS2G enables better performance at subjective risk assessment than rule-based graph extraction methods and deep-learning-based models. RS2G also improves generalization and Sim2Real transfer learning, which denotes the ability to transfer knowledge gained from simulation datasets to unseen real-world scenarios. We also present ablation studies showing how RS2G produces a more useful graph representation for downstream classifiers. Finally, we show how RS2G can identify the relative importance of rule-based graph edges and enables intelligent graph sparsity tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge