Robust Fine-tuning via Perturbation and Interpolation from In-batch Instances
Paper and Code
May 02, 2022
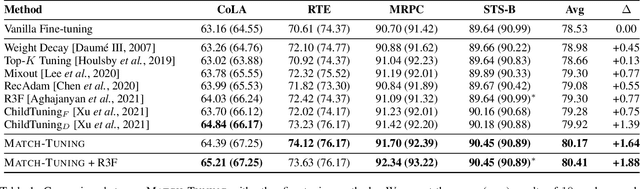

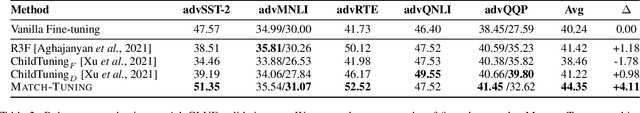
Fine-tuning pretrained language models (PLMs) on downstream tasks has become common practice in natural language processing. However, most of the PLMs are vulnerable, e.g., they are brittle under adversarial attacks or imbalanced data, which hinders the application of the PLMs on some downstream tasks, especially in safe-critical scenarios. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective fine-tuning method called Match-Tuning to force the PLMs to be more robust. For each instance in a batch, we involve other instances in the same batch to interact with it. To be specific, regarding the instances with other labels as a perturbation, Match-Tuning makes the model more robust to noise at the beginning of training. While nearing the end, Match-Tuning focuses more on performing an interpolation among the instances with the same label for better generalization. Extensive experiments on various tasks in GLUE benchmark show that Match-Tuning consistently outperforms the vanilla fine-tuning by $1.64$ scores. Moreover, Match-Tuning exhibits remarkable robustness to adversarial attacks and data imbalance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge