Risk Stratification of Lung Nodules Using 3D CNN-Based Multi-task Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2017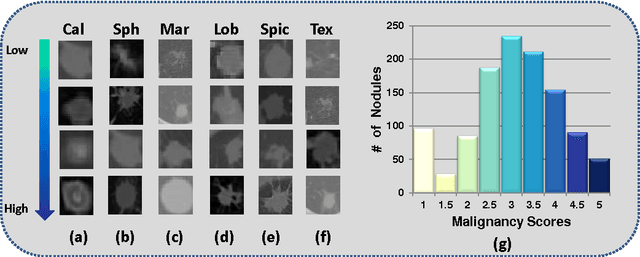

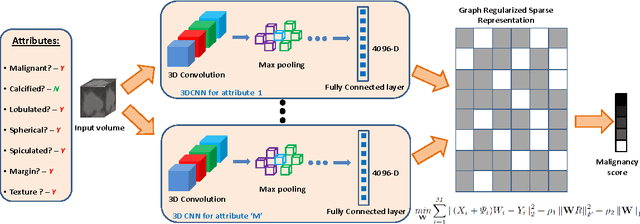
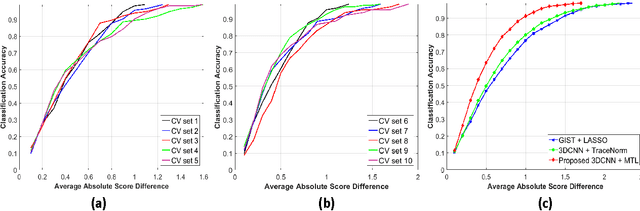
Risk stratification of lung nodules is a task of primary importance in lung cancer diagnosis. Any improvement in robust and accurate nodule characterization can assist in identifying cancer stage, prognosis, and improving treatment planning. In this study, we propose a 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based nodule characterization strategy. With a completely 3D approach, we utilize the volumetric information from a CT scan which would be otherwise lost in the conventional 2D CNN based approaches. In order to address the need for a large amount for training data for CNN, we resort to transfer learning to obtain highly discriminative features. Moreover, we also acquire the task dependent feature representation for six high-level nodule attributes and fuse this complementary information via a Multi-task learning (MTL) framework. Finally, we propose to incorporate potential disagreement among radiologists while scoring different nodule attributes in a graph regularized sparse multi-task learning. We evaluated our proposed approach on one of the largest publicly available lung nodule datasets comprising 1018 scans and obtained state-of-the-art results in regressing the malignancy scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge