Rewiring What-to-Watch-Next Recommendations to Reduce Radicalization Pathways
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2022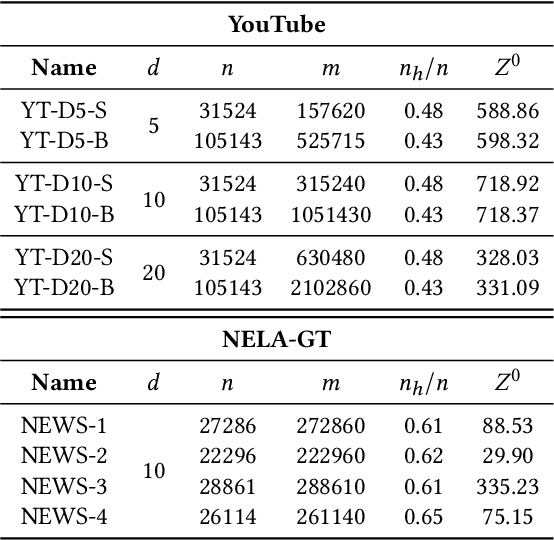
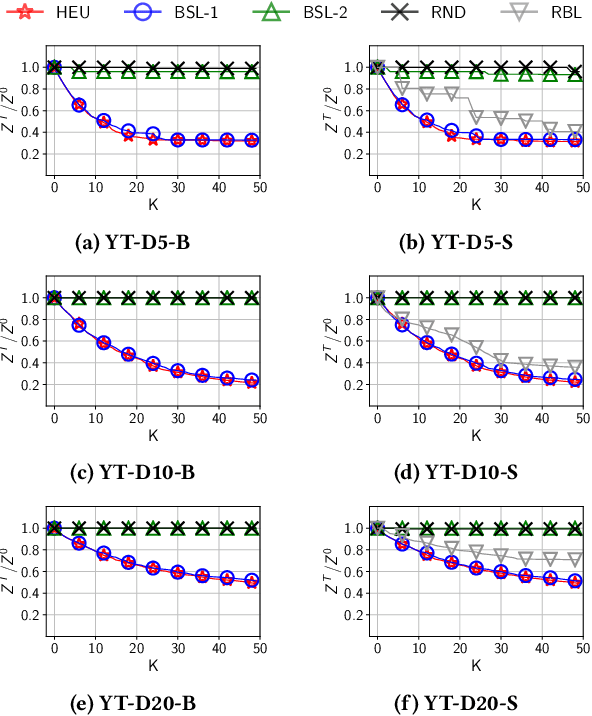
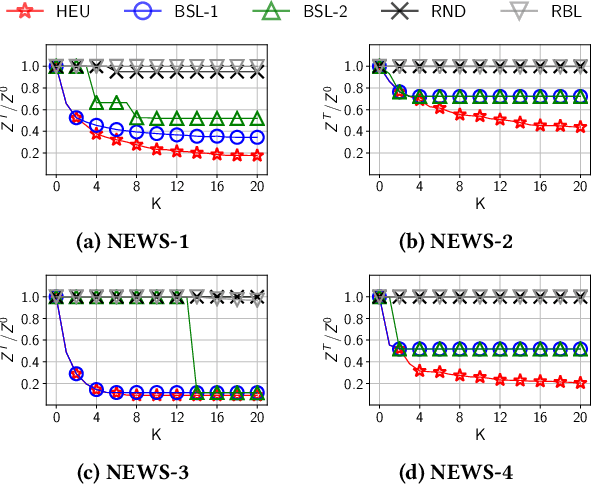
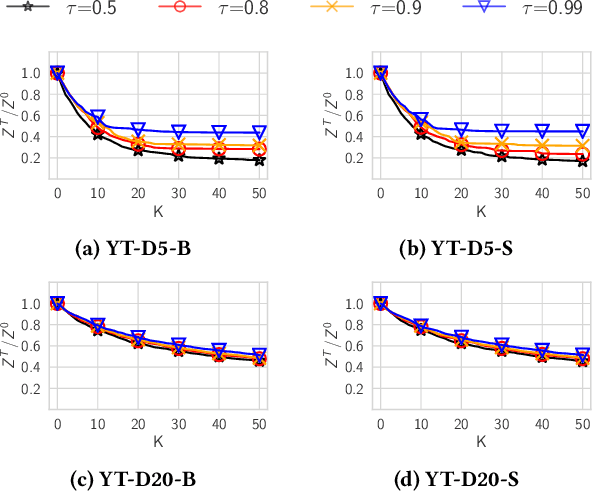
Recommender systems typically suggest to users content similar to what they consumed in the past. If a user happens to be exposed to strongly polarized content, she might subsequently receive recommendations which may steer her towards more and more radicalized content, eventually being trapped in what we call a "radicalization pathway". In this paper, we study the problem of mitigating radicalization pathways using a graph-based approach. Specifically, we model the set of recommendations of a "what-to-watch-next" recommender as a d-regular directed graph where nodes correspond to content items, links to recommendations, and paths to possible user sessions. We measure the "segregation" score of a node representing radicalized content as the expected length of a random walk from that node to any node representing non-radicalized content. High segregation scores are associated to larger chances to get users trapped in radicalization pathways. Hence, we define the problem of reducing the prevalence of radicalization pathways by selecting a small number of edges to "rewire", so to minimize the maximum of segregation scores among all radicalized nodes, while maintaining the relevance of the recommendations. We prove that the problem of finding the optimal set of recommendations to rewire is NP-hard and NP-hard to approximate within any factor. Therefore, we turn our attention to heuristics, and propose an efficient yet effective greedy algorithm based on the absorbing random walk theory. Our experiments on real-world datasets in the context of video and news recommendations confirm the effectiveness of our proposal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge