Rethinking KenLM: Good and Bad Model Ensembles for Efficient Text Quality Filtering in Large Web Corpora
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2024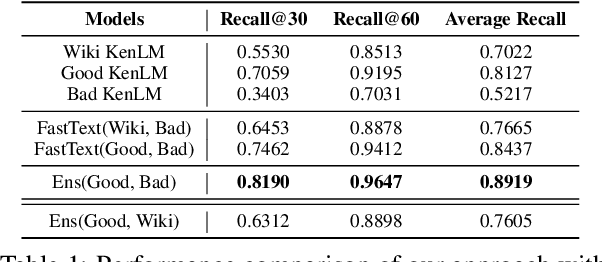
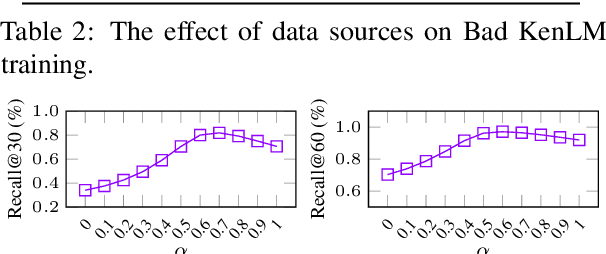
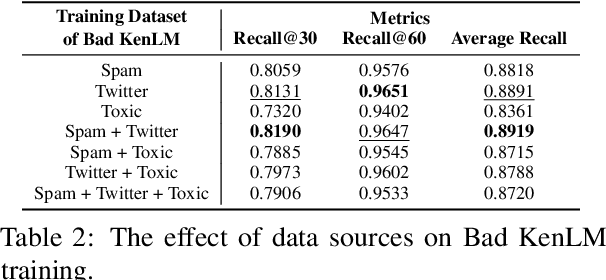

With the increasing demand for substantial amounts of high-quality data to train large language models (LLMs), efficiently filtering large web corpora has become a critical challenge. For this purpose, KenLM, a lightweight n-gram-based language model that operates on CPUs, is widely used. However, the traditional method of training KenLM utilizes only high-quality data and, consequently, does not explicitly learn the linguistic patterns of low-quality data. To address this issue, we propose an ensemble approach that leverages two contrasting KenLMs: (i) Good KenLM, trained on high-quality data; and (ii) Bad KenLM, trained on low-quality data. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces noisy content while preserving high-quality content compared to the traditional KenLM training method. This indicates that our method can be a practical solution with minimal computational overhead for resource-constrained environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge