Recurrent Embedding Aggregation Network for Video Face Recognition
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2019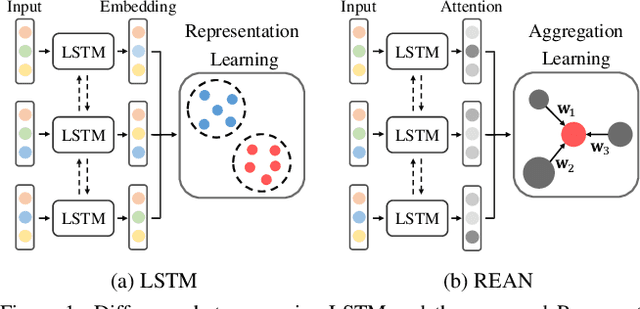
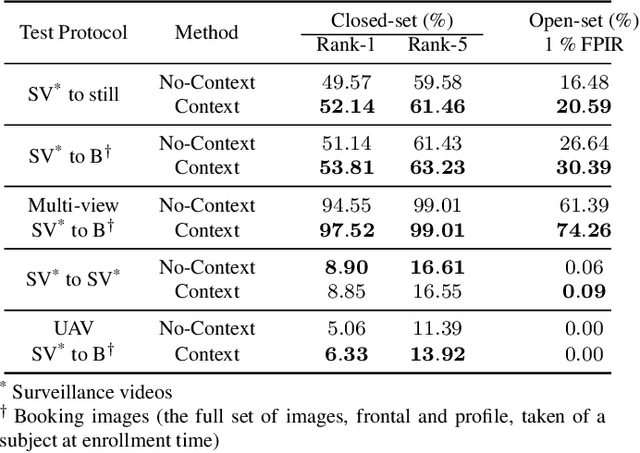

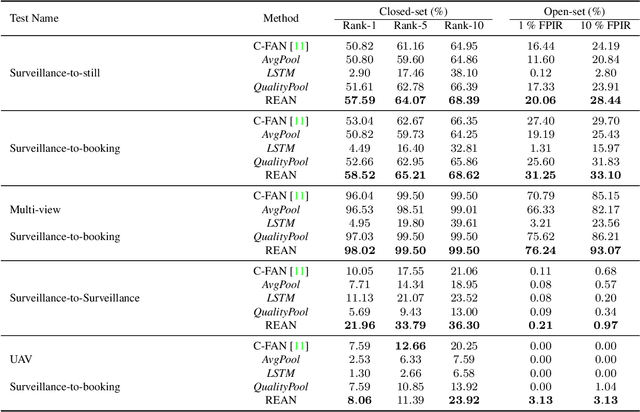
Recurrent networks have been successful in analyzing temporal data and have been widely used for video analysis. However, for video face recognition, where the base CNNs trained on large-scale data already provide discriminative features, using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), a popular recurrent network, for feature learning could lead to overfitting and degrade the performance instead. We propose a Recurrent Embedding Aggregation Network (REAN) for set to set face recognition. Compared with LSTM, REAN is robust against overfitting because it only learns how to aggregate the pre-trained embeddings rather than learning representations from scratch. Compared with quality-aware aggregation methods, REAN can take advantage of the context information to circumvent the noise introduced by redundant video frames. Empirical results on three public domain video face recognition datasets, IJB-S, YTF, and PaSC show that the proposed REAN significantly outperforms naive CNN-LSTM structure and quality-aware aggregation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge