Real-world Machine Learning Systems: A survey from a Data-Oriented Architecture Perspective
Paper and Code
Feb 09, 2023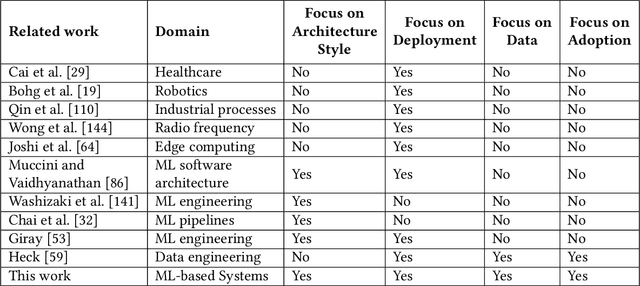
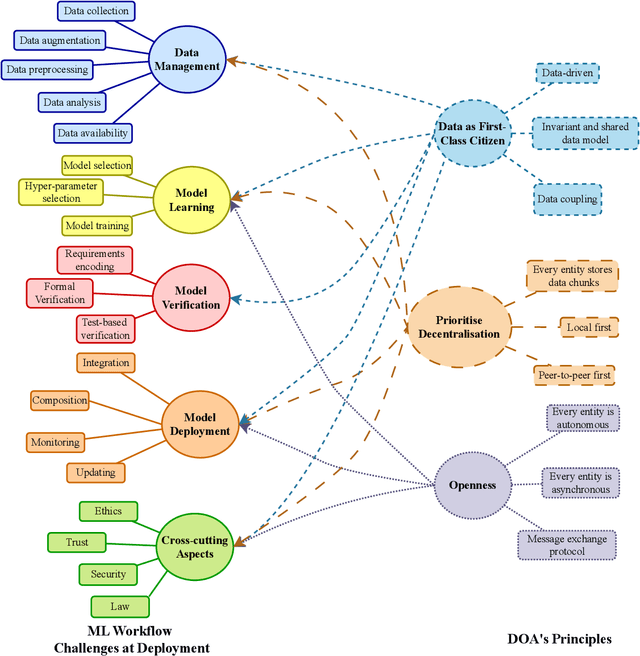
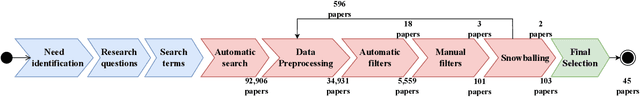

With the upsurge of interest in artificial intelligence machine learning (ML) algorithms, originally developed in academic environments, are now being deployed as parts of real-life systems that deal with large amounts of heterogeneous, dynamic, and high-dimensional data. Deployment of ML methods in real life is prone to challenges across the whole system life-cycle from data management to systems deployment, monitoring, and maintenance. Data-Oriented Architecture (DOA) is an emerging software engineering paradigm that has the potential to mitigate these challenges by proposing a set of principles to create data-driven, loosely coupled, decentralised, and open systems. However DOA as a concept is not widespread yet, and there is no common understanding of how it can be realised in practice. This review addresses that problem by contextualising the principles that underpin the DOA paradigm through the ML system challenges. We explore the extent to which current architectures of ML-based real-world systems have implemented the DOA principles. We also formulate open research challenges and directions for further development of the DOA paradigm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge