Real-Time Asphalt Pavement Layer Thickness Prediction Using Ground-Penetrating Radar Based on a Modified Extended Common Mid-Point (XCMP) Approach
Paper and Code
Jan 07, 2024
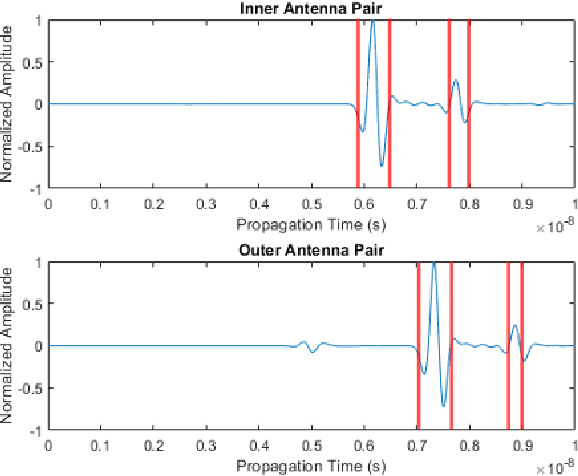


The conventional surface reflection method has been widely used to measure the asphalt pavement layer dielectric constant using ground-penetrating radar (GPR). This method may be inaccurate for in-service pavement thickness estimation with dielectric constant variation through the depth, which could be addressed using the extended common mid-point method (XCMP) with air-coupled GPR antennas. However, the factors affecting the XCMP method on thickness prediction accuracy haven't been studied. Manual acquisition of key factors is required, which hinders its real-time applications. This study investigates the affecting factors and develops a modified XCMP method to allow automatic thickness prediction of in-service asphalt pavement with non-uniform dielectric properties through depth. A sensitivity analysis was performed, necessitating the accurate estimation of time of flights (TOFs) from antenna pairs. A modified XCMP method based on edge detection was proposed to allow real-time TOFs estimation, then dielectric constant and thickness predictions. Field tests using a multi-channel GPR system were performed for validation. Both the surface reflection and XCMP setups were conducted. Results show that the modified XCMP method is recommended with a mean prediction error of 1.86%, which is more accurate than the surface reflection method (5.73%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge