Ray-Based and Graph-Based Methods for Fiber Bundle Boundary Estimation
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2011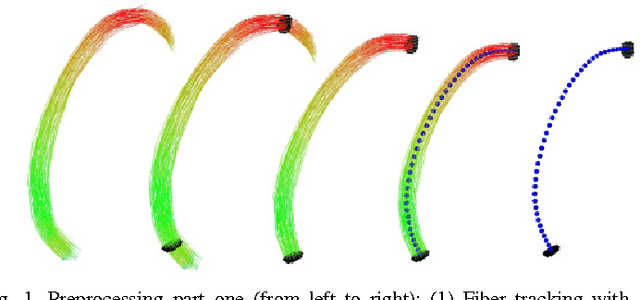
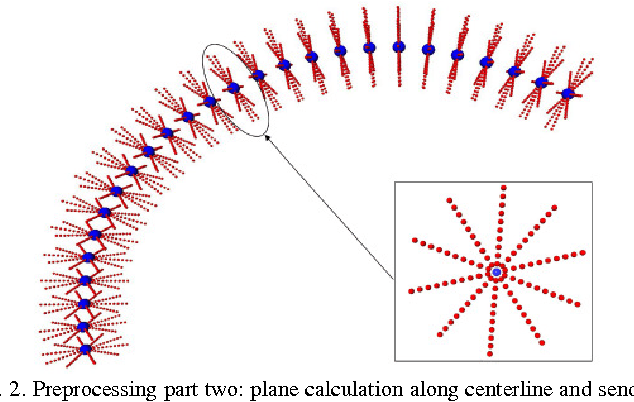
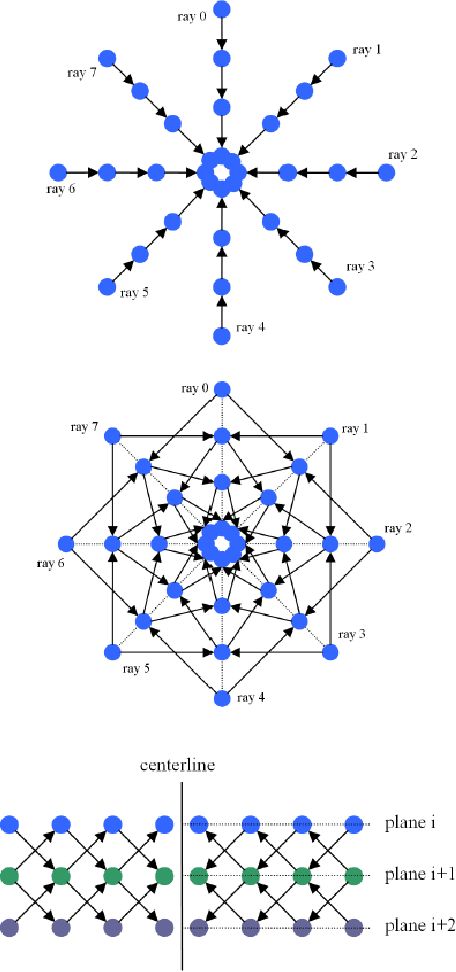
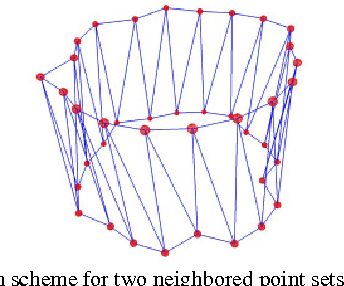
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) provides the possibility of estimating the location and course of eloquent structures in the human brain. Knowledge about this is of high importance for preoperative planning of neurosurgical interventions and for intraoperative guidance by neuronavigation in order to minimize postoperative neurological deficits. Therefore, the segmentation of these structures as closed, three-dimensional object is necessary. In this contribution, two methods for fiber bundle segmentation between two defined regions are compared using software phantoms (abstract model and anatomical phantom modeling the right corticospinal tract). One method uses evaluation points from sampled rays as candidates for boundary points, the other method sets up a directed and weighted (depending on a scalar measure) graph and performs a min-cut for optimal segmentation results. Comparison is done by using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), a measure for spatial overlap of different segmentation results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge