Ranking Scientific Papers Using Preference Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 02, 2021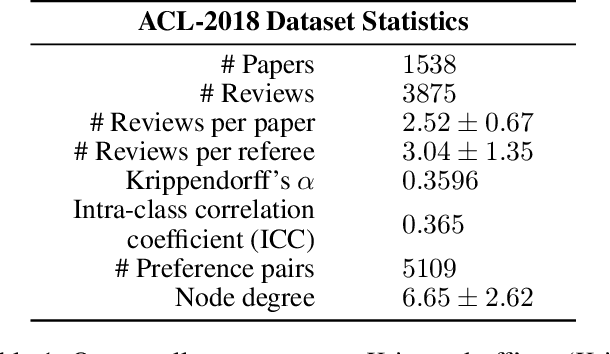
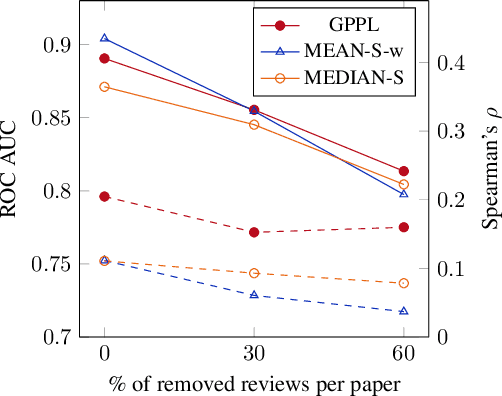
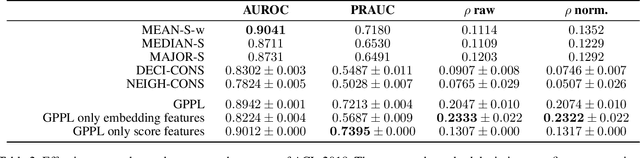
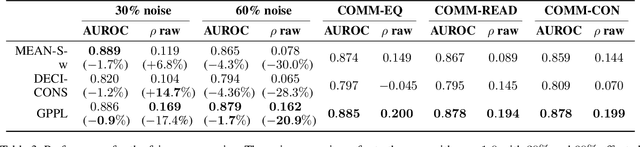
Peer review is the main quality control mechanism in academia. Quality of scientific work has many dimensions; coupled with the subjective nature of the reviewing task, this makes final decision making based on the reviews and scores therein very difficult and time-consuming. To assist with this important task, we cast it as a paper ranking problem based on peer review texts and reviewer scores. We introduce a novel, multi-faceted generic evaluation framework for making final decisions based on peer reviews that takes into account effectiveness, efficiency and fairness of the evaluated system. We propose a novel approach to paper ranking based on Gaussian Process Preference Learning (GPPL) and evaluate it on peer review data from the ACL-2018 conference. Our experiments demonstrate the superiority of our GPPL-based approach over prior work, while highlighting the importance of using both texts and review scores for paper ranking during peer review aggregation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge