Rain Rate Estimation with SAR using NEXRAD measurements with Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2022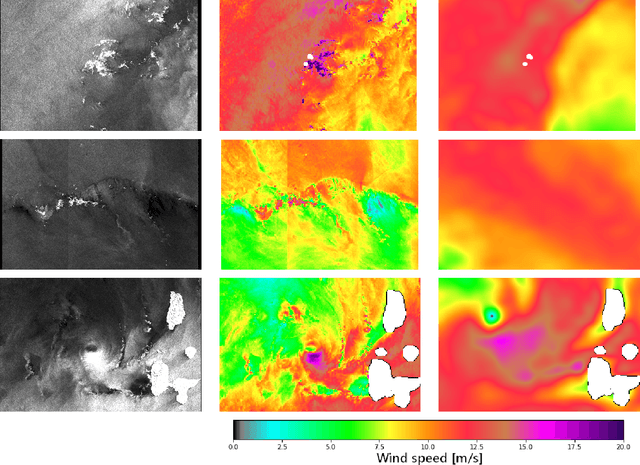
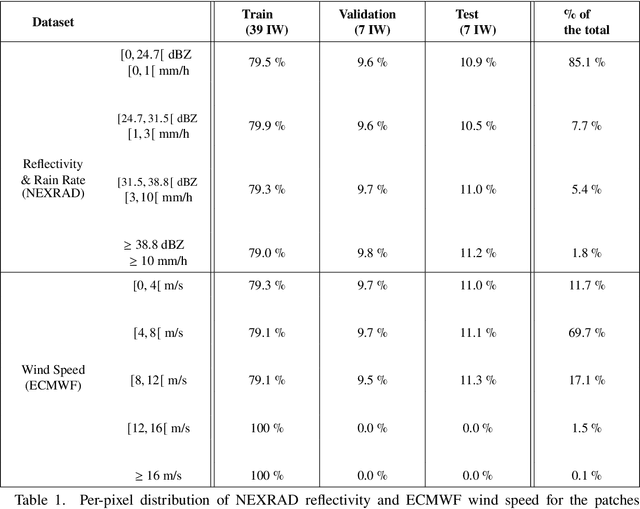
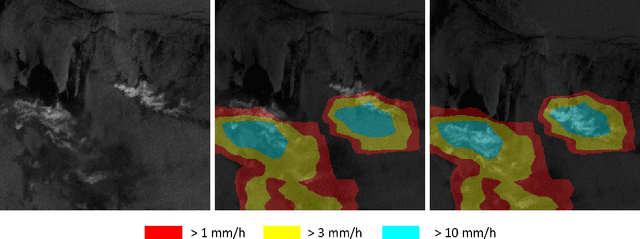
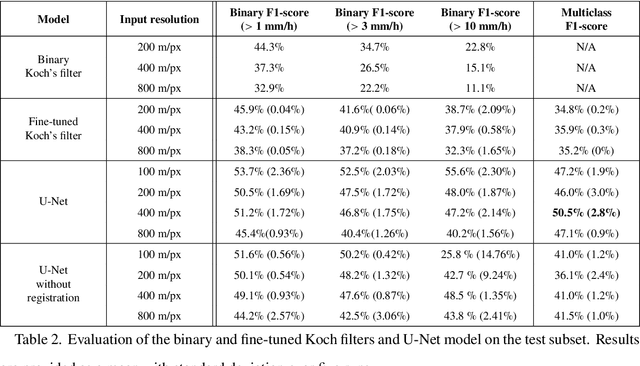
Remote sensing of rainfall events is critical for both operational and scientific needs, including for example weather forecasting, extreme flood mitigation, water cycle monitoring, etc. Ground-based weather radars, such as NOAA's Next-Generation Radar (NEXRAD), provide reflectivity and precipitation measurements of rainfall events. However, the observation range of such radars is limited to a few hundred kilometers, prompting the exploration of other remote sensing methods, paricularly over the open ocean, that represents large areas not covered by land-based radars. For a number of decades, C-band SAR imagery such a such as Sentinel-1 imagery has been known to exhibit rainfall signatures over the sea surface. However, the development of SAR-derived rainfall products remains a challenge. Here we propose a deep learning approach to extract rainfall information from SAR imagery. We demonstrate that a convolutional neural network, such as U-Net, trained on a colocated and preprocessed Sentinel-1/NEXRAD dataset clearly outperforms state-of-the-art filtering schemes. Our results indicate high performance in segmenting precipitation regimes, delineated by thresholds at 1, 3, and 10 mm/h. Compared to current methods that rely on Koch filters to draw binary rainfall maps, these multi-threshold learning-based models can provide rainfall estimation for higher wind speeds and thus may be of great interest for data assimilation weather forecasting or for improving the qualification of SAR-derived wind field data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge