R2-Trans:Fine-Grained Visual Categorization with Redundancy Reduction
Paper and Code
Apr 21, 2022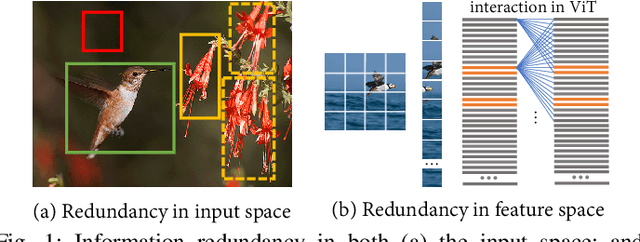
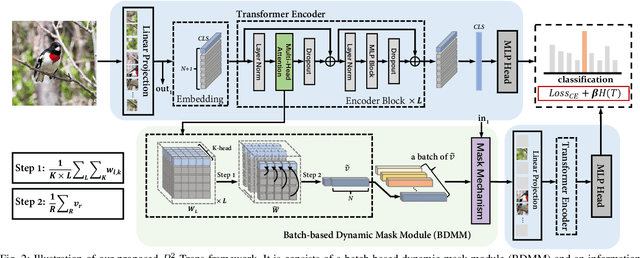
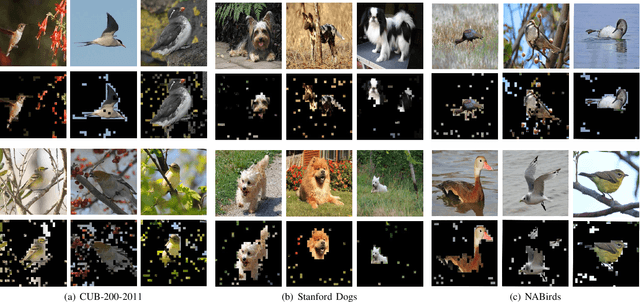
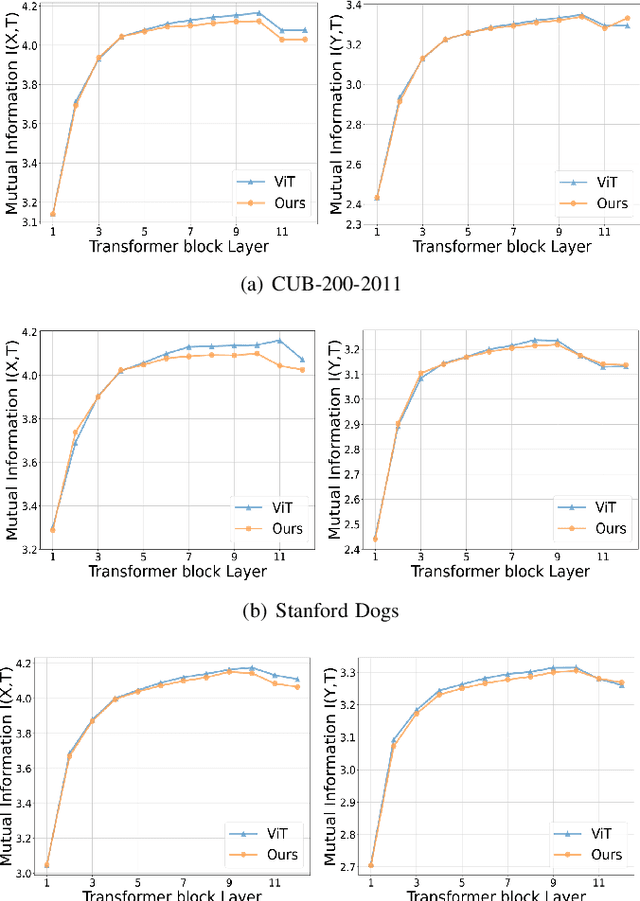
Fine-grained visual categorization (FGVC) aims to discriminate similar subcategories, whose main challenge is the large intraclass diversities and subtle inter-class differences. Existing FGVC methods usually select discriminant regions found by a trained model, which is prone to neglect other potential discriminant information. On the other hand, the massive interactions between the sequence of image patches in ViT make the resulting class-token contain lots of redundant information, which may also impacts FGVC performance. In this paper, we present a novel approach for FGVC, which can simultaneously make use of partial yet sufficient discriminative information in environmental cues and also compress the redundant information in class-token with respect to the target. Specifically, our model calculates the ratio of high-weight regions in a batch, adaptively adjusts the masking threshold and achieves moderate extraction of background information in the input space. Moreover, we also use the Information Bottleneck~(IB) approach to guide our network to learn a minimum sufficient representations in the feature space. Experimental results on three widely-used benchmark datasets verify that our approach can achieve outperforming performance than other state-of-the-art approaches and baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge