Q-Net: Query-Informed Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2022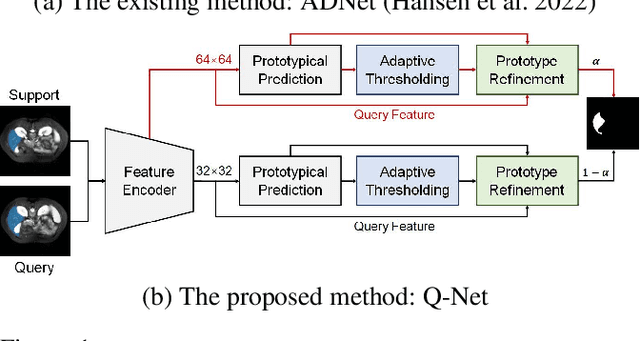
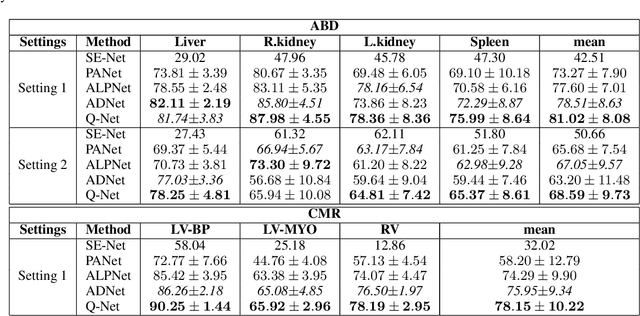
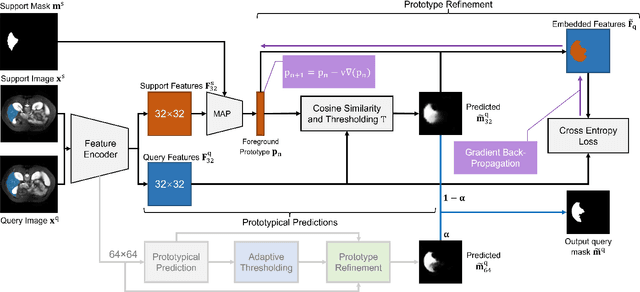
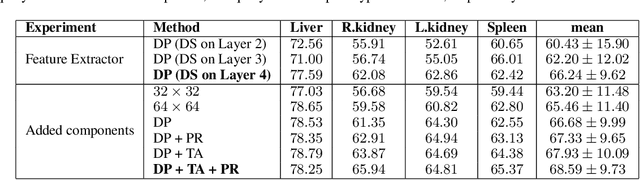
Deep learning has achieved tremendous success in computer vision, while medical image segmentation (MIS) remains a challenge, due to the scarcity of data annotations. Meta-learning techniques for few-shot segmentation (Meta-FSS) have been widely used to tackle this challenge, while they neglect possible distribution shifts between the query image and the support set. In contrast, an experienced clinician can perceive and address such shifts by borrowing information from the query image, then fine-tune or calibrate his (her) prior cognitive model accordingly. Inspired by this, we propose Q-Net, a Query-informed Meta-FSS approach, which mimics in spirit the learning mechanism of an expert clinician. We build Q-Net based on ADNet, a recently proposed anomaly detection-inspired method. Specifically, we add two query-informed computation modules into ADNet, namely a query-informed threshold adaptation module and a query-informed prototype refinement module. Combining them with a dual-path extension of the feature extraction module, Q-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance on two widely used datasets, which are composed of abdominal MR images and cardiac MR images, respectively. Our work sheds light on a novel way to improve Meta-FSS techniques by leveraging query information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge