Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy Classification Using its Temporal Evolution with Two-Stream 3D Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
May 22, 2020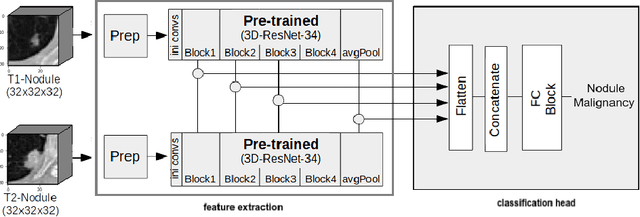
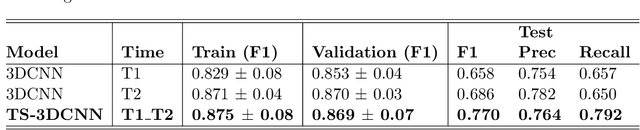
Nodule malignancy assessment is a complex, time-consuming and error-prone task. Current clinical practice requires measuring changes in size and density of the nodule at different time-points. State of the art solutions rely on 3D convolutional neural networks built on pulmonary nodules obtained from single CT scan per patient. In this work, we propose a two-stream 3D convolutional neural network that predicts malignancy by jointly analyzing two pulmonary nodule volumes from the same patient taken at different time-points. Best results achieve 77% of F1-score in test with an increment of 9% and 12% of F1-score with respect to the same network trained with images from a single time-point.
View paper on
 OpenReview
OpenReview
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge